2017
1. Yang SD, Chen L, Wang C, Rana M, Ma PC*. Surface roughness induced superhydrophobicity of graphene foam for oil-water separation. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2017, 508, 254-262.
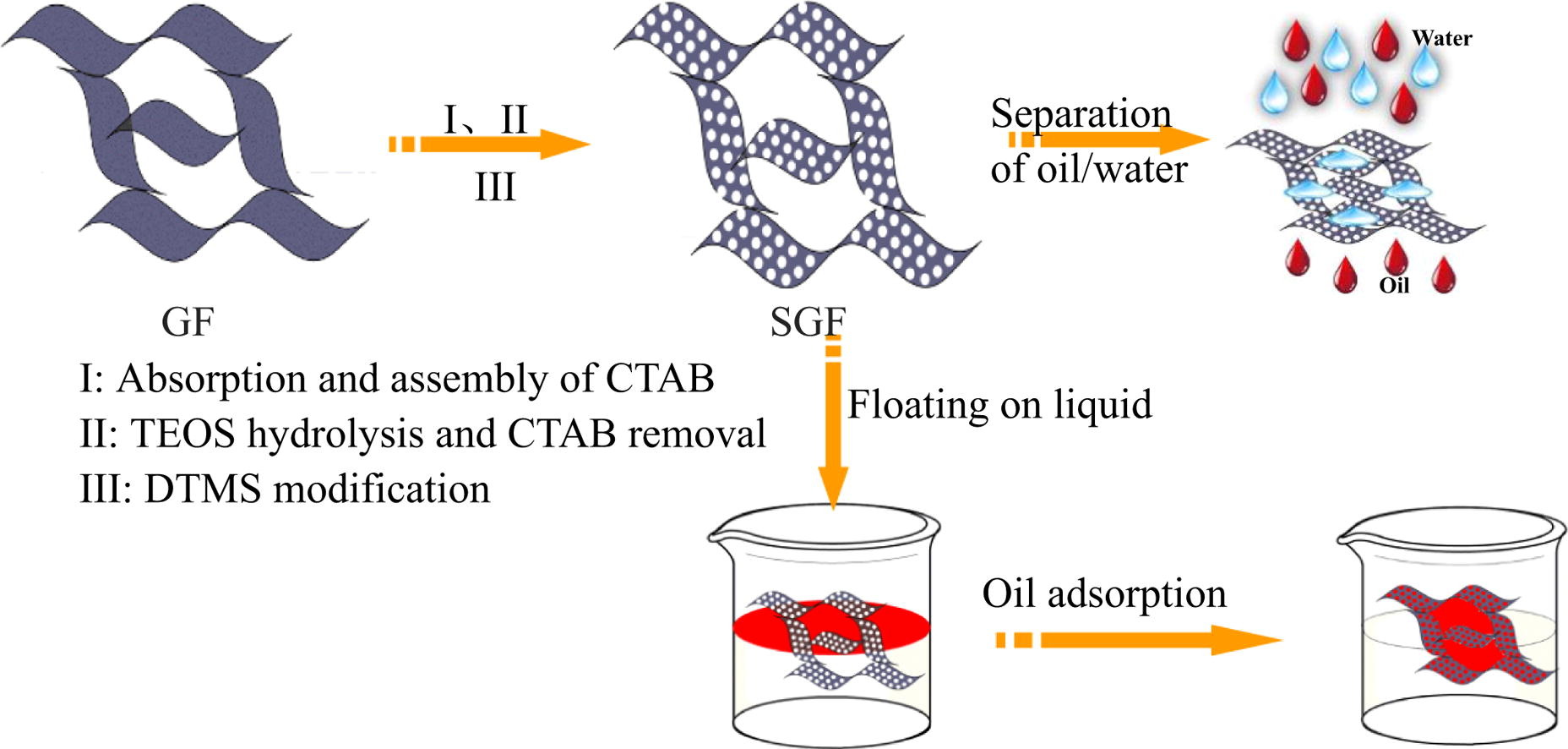
■ Graphene foam with superhydrophobic and oleophilic properties was prepared by incorporating silica nanoparticles onto graphene sheet via sol-gel method and subsequent modification using silane. Superhydrophobic foam can adsorb a broad variety of oil liquids with enormous adsorption capacities and excellent recyclability, and can be effectively applied to separate oil-water mixture.
2. Hao B, Förster T, Mäder E, Ma PC*. Modification of basalt fiber using pyrolytic carbon coating for sensing application. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2017, 101, 123-128.
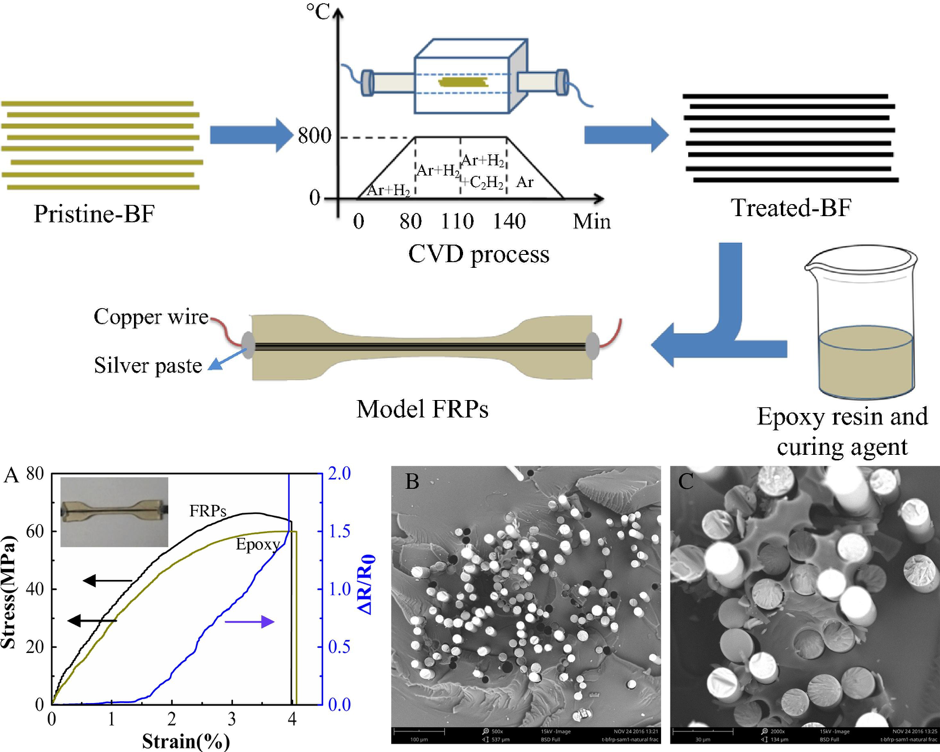
■ The modification of basalt fiber (BF) using a chemical vapor deposition (CVD) method was successfully reported with the aim of enhancing the functionality of BF for sensing applications. The results showed that the coated BF showed electrical conductivity as well as increased the tensile strength.
3. Wang CC, Yang S, Ma Q, Jia X*, Ma PC*. Preparation of carbon nanotubes/graphene hybrid aerogel and its application for the adsorption of organic compounds. Carbon, 2017, 118, 765-771.
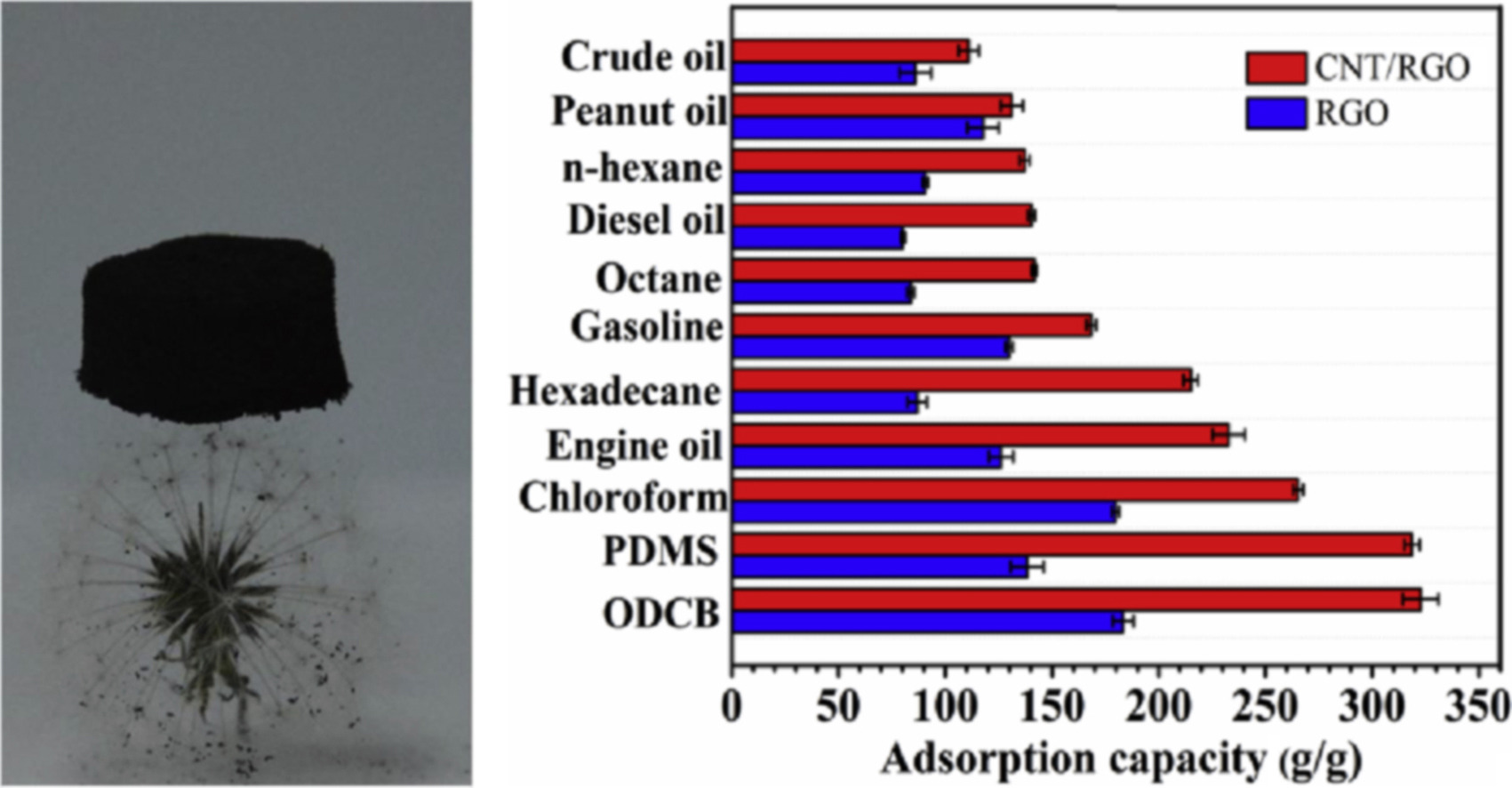
■ A hybrid aerogel consisting of carbon nanotubes (CNTs) and graphene was prepared. The growth of CNTs on the graphene sheets in the hybrid aerogel endowed the material a hierarchical structure with low density, excellent hydrophobicity and oleophilicity to the organic compounds. The aerogel can adsorb a variety of oily liquids with outstanding reusability.
4. Rana M, Asim S, Hao B, Yang S, Ma PC*. Carbon nanotubes on highly interconnected carbonized cotton for flexible and light-weight energy storage. Advanced Sustainable System, 2017, 1700022.

■ A facile strategy to synthesize disordered CNTs on carbonized cotton gauze by a single-step CVD method was reported. The obtained electrochemical performances of material were the highest ones among currently reported pure carbon-based supercapacitors and also comparable with that of hybrid supercapacitors consisting of carbon/polymers and carbon/transition-metal oxides.
5. Chen JT, Shen CH, Yang SD, Masud R, Ma PC*. Acid and temperature dual-responsive cotton fabrics with polymer coating. Composites Communications, 2017, 4, 10-15.
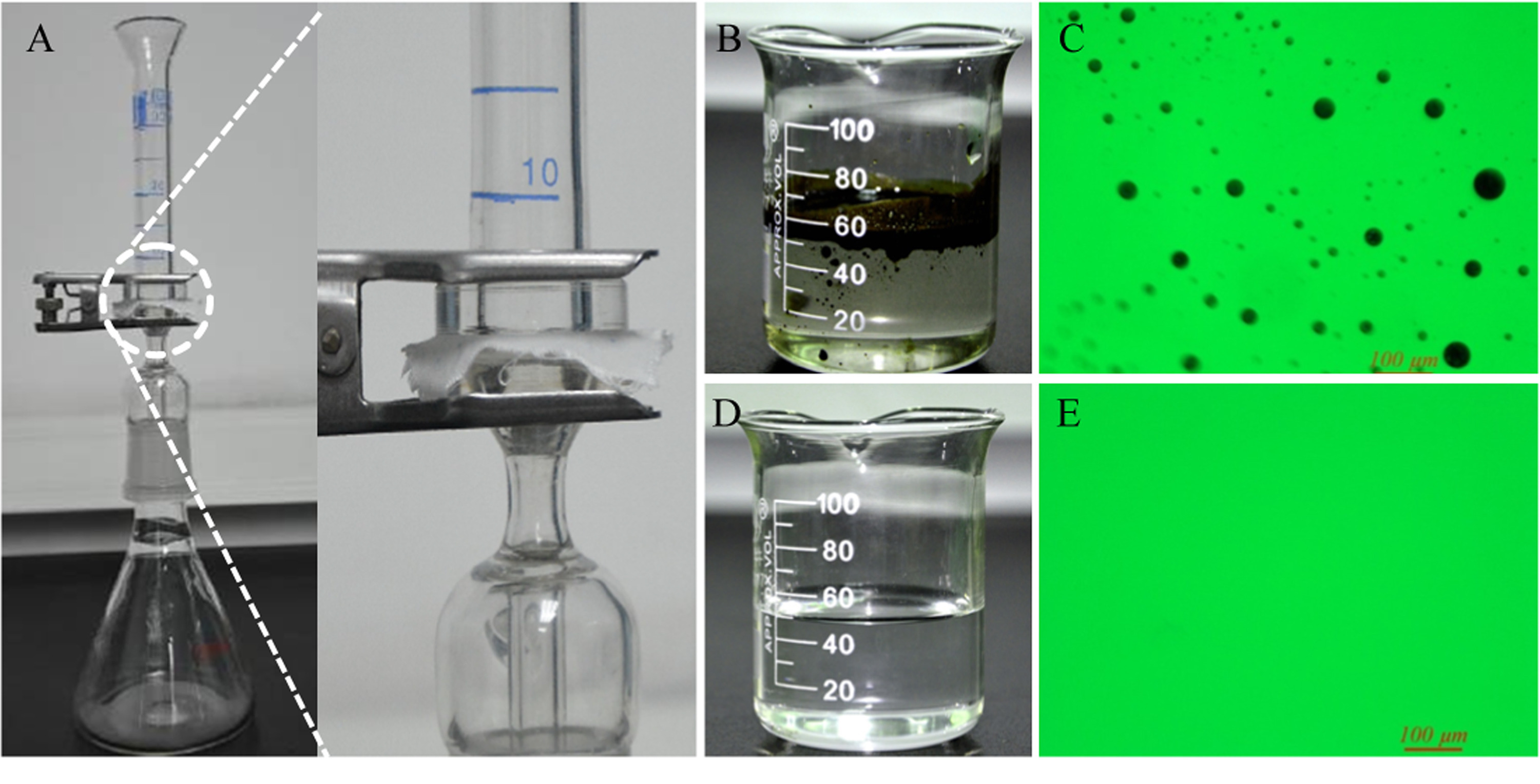
■ Cotton-based fabrics with dual responses to pH and temperature were successfully fabricated, by applying a thin layer of copolymer originated from N-isopropylacrylamide and acrylic acid. The prepared CFs showed controlled water permeability under different chemical and environmental conditions. The textile can selectively separate water from crude oil-water mixtures.
6. Kang X, Wang C, Yin J*. Hierarchically Porous Carbons Derived from Cotton Stalks for High-Performance Supercapacitors. Chemelectrochem,2017, 4 , 2599-2607.

■ A simple and cost-effective method for the synthesis of hierarchically porous carbons from cotton stalks (CSs) with H3PO4 activation is reported. The resulting material presents a higher surface area utilization rate than other CS-derived porous carbons, a high specific capacitance in alkaline solution, an excellent rate capability and long-term stability.
7. Li H, Ye H, Xu Z, Wang C, Yin J*, Zhu H*. Freestanding MoO2/Mo2C imbedded carbon fibers for Li-ion batteries. Physical Chemistry Chemical Phyisics.,2017, 19, 2908-2914.
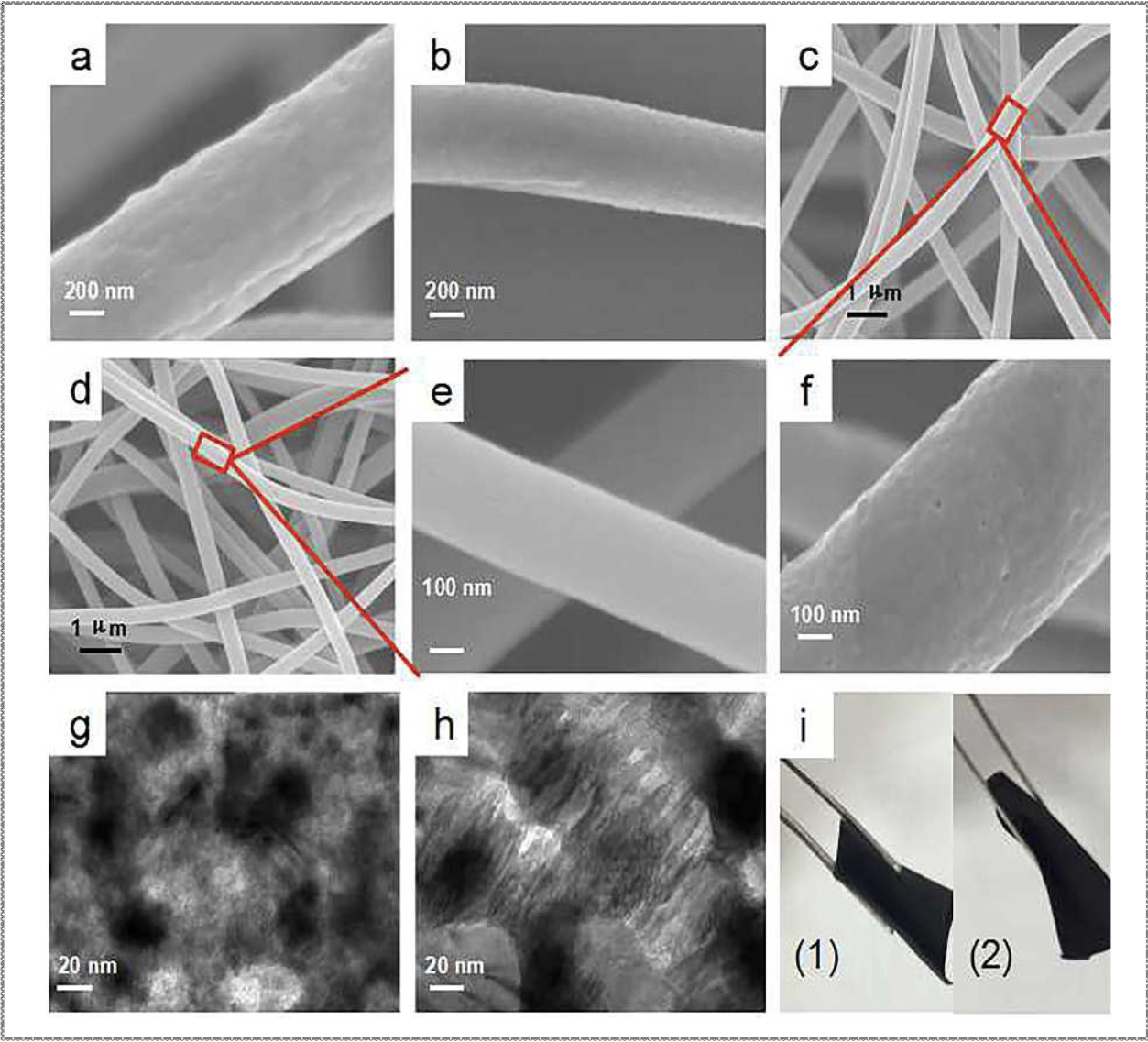
■ A highly porous MoO2/Mo2C imbedded carbon fibers (MoO2/Mo2C ICFs) have been successfully synthesized from two types of Mo precursors. It can be concluded from the electrochemical measurements that the as-synthesized flexible MoO2/Mo2C ICFs manifest remarkable advantages in terms of rate and long cycling performance.
8. Xu Z, Ye H, Li H, Xu Y, Wang C, Yin J*, Zhu H*. Enhanced Lithium Ion Storage Performance of Tannic Acid in LiTFSI Electrolyte. ACS Omega,2017, 2, 1273-1278.
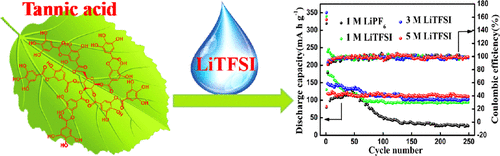
■ Tannic acid (TA) has been proposed as a desirable organic anode material for lithium ion batteries (LIBs). Through the integration of chemical analyses with electrochemical characterizations, TA has been validated as a promising anode material for LIBs, benefiting from the abundant existence of oxygen-containing functionalities and the correlated redox reactions.
附件下载: