2022
1. Lv CJ, Hao B, Yasin A*, Yue X, Ma PC*. H2O2-assisted preparation of superhydrophilic polyacrylonitrile fabric and its application for the separation of oil/water mixture. Colloids and Surface A-Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2022, 646, 129004. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2022.129004.
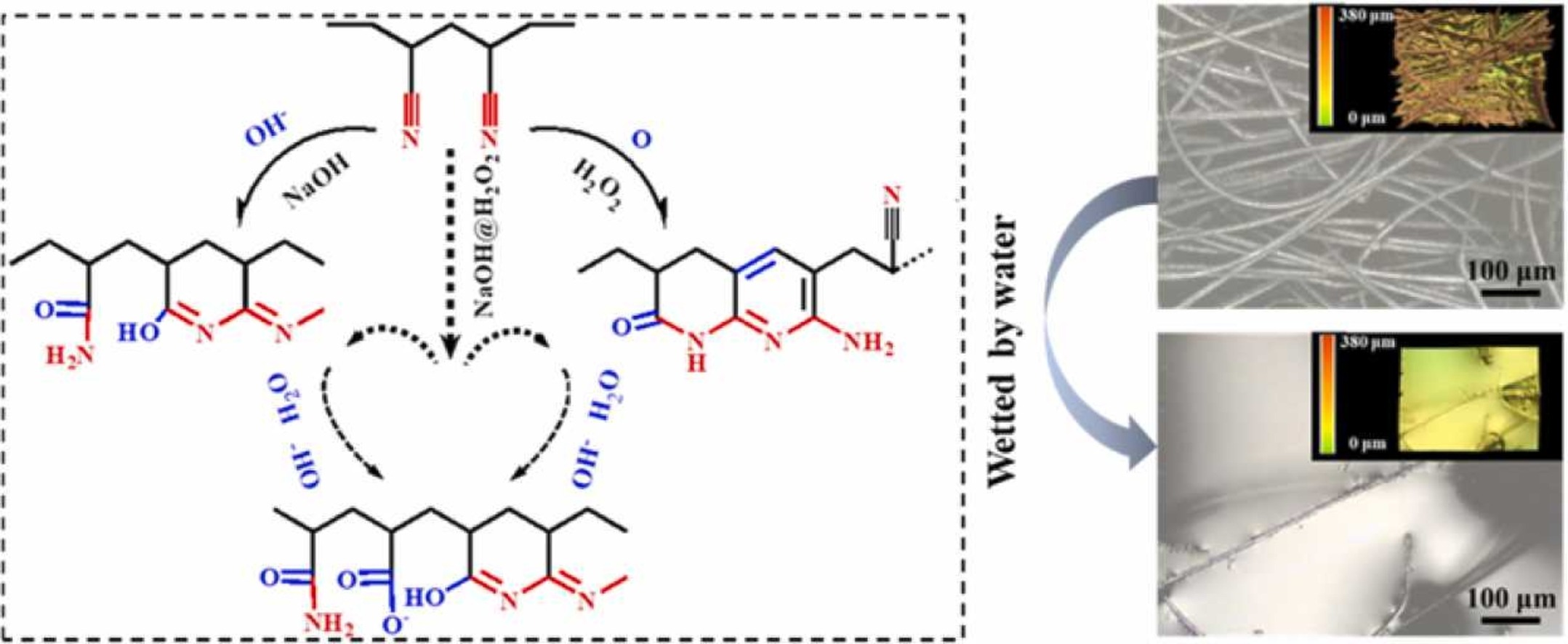
■ A superhydrophilic polyacrylonitrile non-woven fabric treated with a low concentration of NaOH@H2O2 mixture for efficiently separating oil/water mixtures was reported. The mechanism of hydrophilic modification was investigated in detail.
2. Lv CJ, Hao B, Yasin A**, Yue X, Ma PC*. Molecular and structural design of polyacrylonitrile-based membrane for oil-water separation. Polymer, 2022, 253, 124969. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2022.124969.
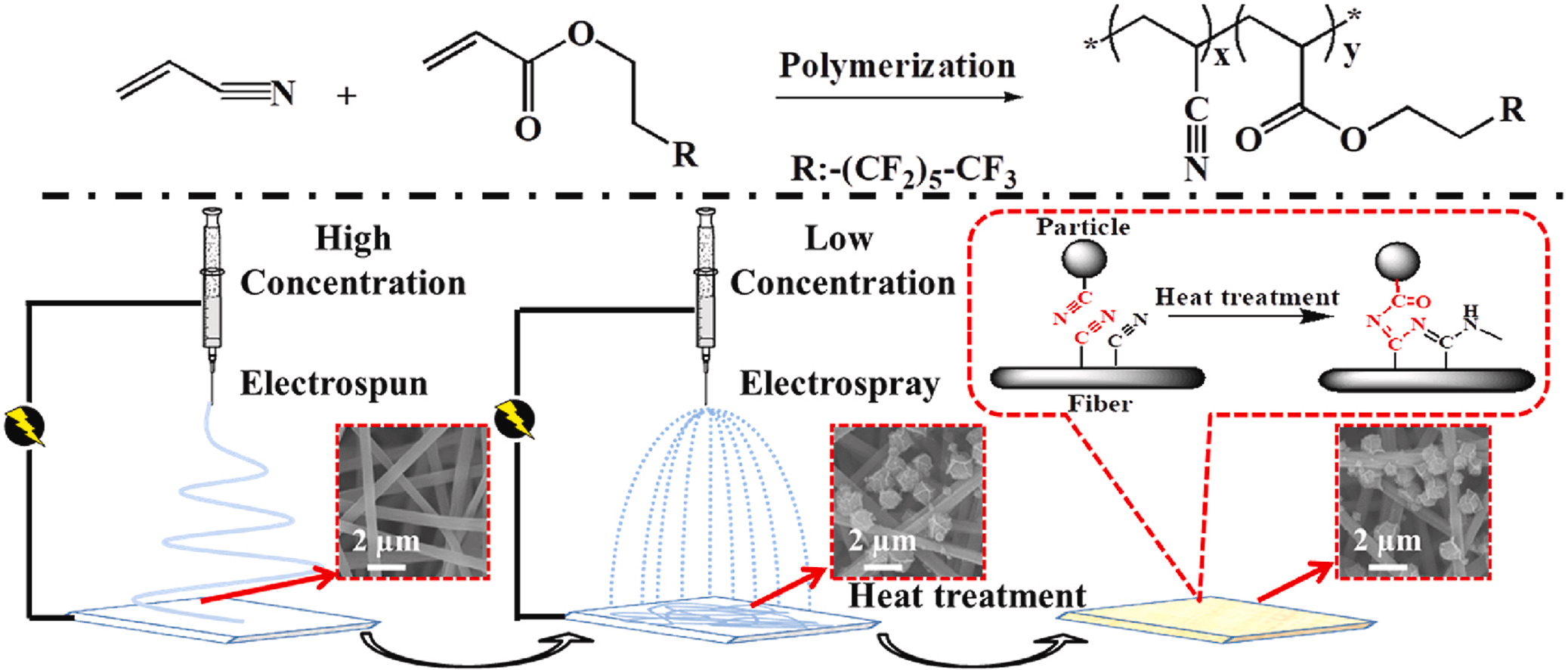
■ A copolymer was synthesized from acrylonitrile (AN) and fluorinated acrylate via radical polymerization, then used to develop a superhydrophobic membrane through electrospinning/electrospraying and subsequent heat treatment. The durability and efficiency of the membrane in separating different oil-water mixtures were demonstrated.
3. Lv CJ, Li H, Yasin A*, Hao B, Yue X, Ma PC*. Preparation of superhydrophilic poly(acrylonitrile/acrylic acid) electrospun membrane and its application in oil/water separation. Polymer, 2022, 258, 125292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2022.125292.
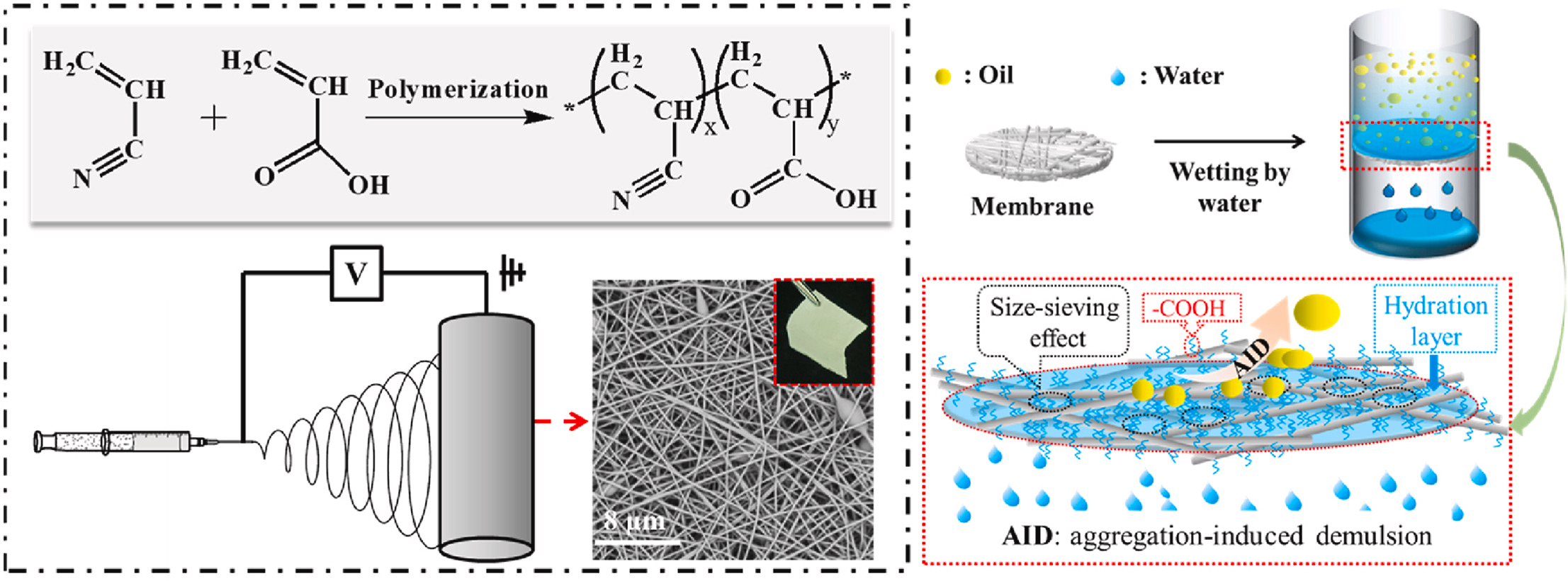
■ A variety of copolymers with different molar ratios of acrylonitrile (AN) and acrylic acid (AA) were synthesized to produce ENF membranes. Among these, the ENF membrane comprising a copolymer with 20 mol% AA exhibited superior wettability and water adsorption ratio. Additionally, this membrane displayed outstanding mechanical properties, anti-fouling ability, and separation efficiency for diverse oil/water mixtures and oil-in-water emulsions.
4. Dou YL, Yue X, Lv CJ, Yasin A, Hao B, Su Y*, Ma PC*. Dual-responsive polyacrylonitrile-based electrospun membrane for controllable oil-water separation. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2022, 438, 129565. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2022.129565.
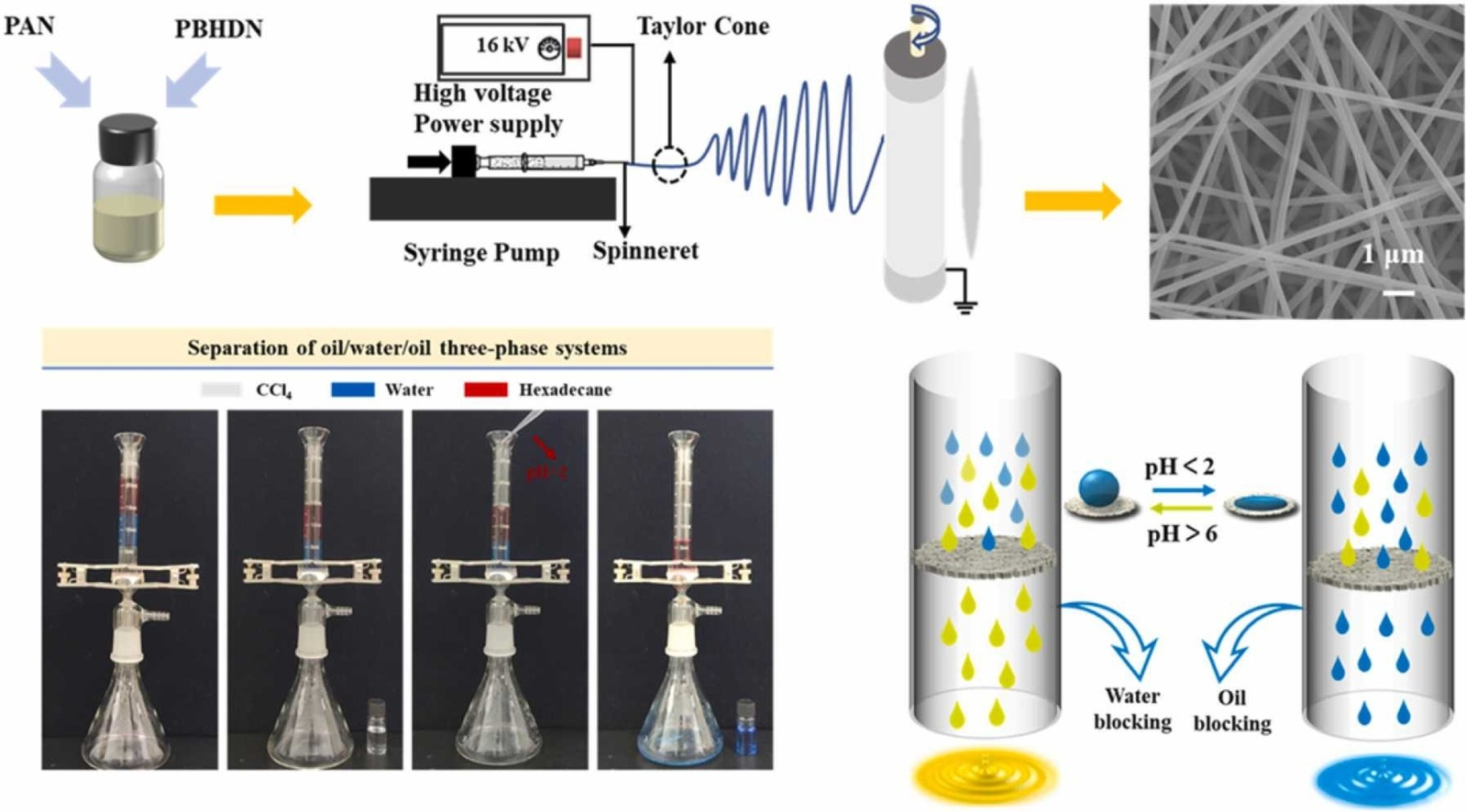
■ A composite membrane was developed by synthesizing a responsive copolymer from N-isopropylacrylamide and 2-(dimethylamino)ethyl methacrylate and electrospinning it with polyacrylonitrile. The membrane’s response to external stimuli was evaluated by examining changes in wettability with water and hydrostatic pressure under varying conditions. The mechanism underlying the stimuli-responsive behavior was elucidated.
5. Yang FH, Hao B, Yue X*, Ma PC*. Fluorescence and stimuli-responsive performance of polymer composites filled with tetraphenylethene derivatives. Polymer Chemistry, 2022, 13, 3126-3135. https://doi.org/10.1039/d2py00396a.
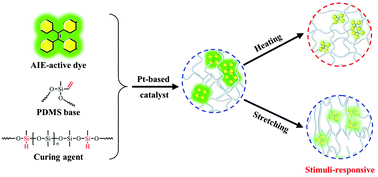
■ A series of tetraphenylethene (TPE)-based derivatives with varying numbers of 3-butenloxy groups were synthesized. The impact of substituent numbers on the fluorescence properties of TPE was reported both experimentally and theoretically. These derivatives were then integrated into a polymer matrix to develop AIE-active composites, and their fluorescence behavior under thermal and mechanical stimuli was examined. The study also elucidated the mechanism underlying the response of the developed composites to external stimuli.
6. Ma FX, Hao B*, Xi XY, Wang R, Ma PC**. Aggregation-induced demulsification technology for the separation of highly emulsified oily wastewater produced in the petrochemical industry. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2022, 374, 134017. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.134017.
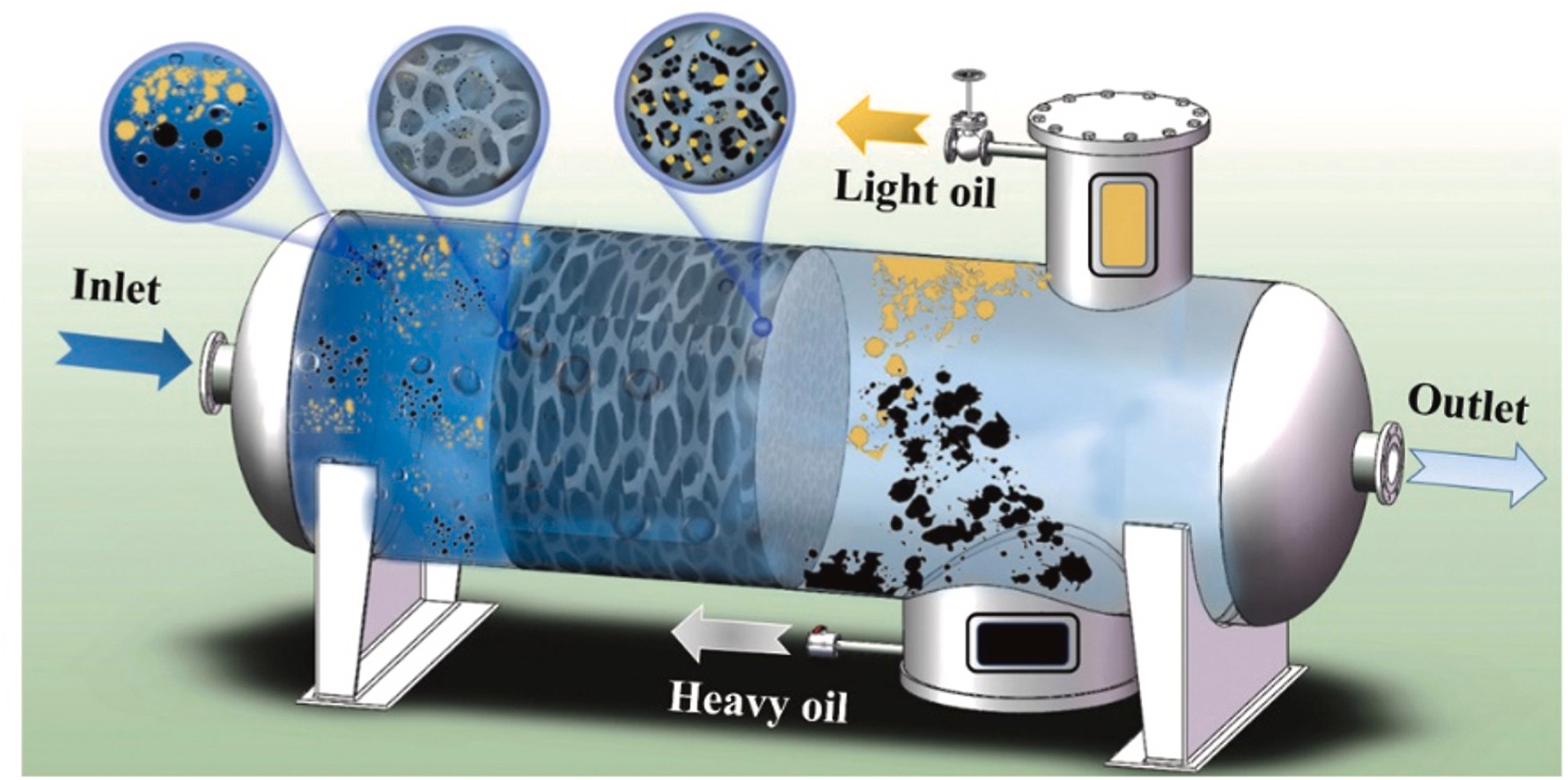
■ An aggregation-induced demulsification (AID) technology utilizing multi-stage packed beds filled with polyurethane sponge was developed for treating oily wastewater from the petrochemical industry. Industrial-scale testing demonstrated significant COD reduction and efficient oil removal, achieving an average COD of 329 mg/L and 93.52% oil removal efficiency at flow rates of 600–1300 L/h. The AID process offers environmental benefits with zero chemical consumption and a simplified treatment process, providing a cleaner solution for oily wastewater treatment.
7. Zhang LS, Yasin A*, Li M, Hao B, Ma PC*. Silicate based solar evaporator with self-cleaning and corrosion resistant properties for durable seawater desalination. Sustainable Materials and Technologies, 2021, 30, e00362. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.susmat.2021.e00362.

■ A silicate-based solar evaporator featuring a polypyrrole-modified commercial sand core and basalt fiber was developed for highly efficient solar steam generation. The silicate-based substrate ensures mechanical strength and stability in seawater, highlighting its potential for reliable solar steam generation. This evaporator demonstrated high efficiency, with an 85.9% evaporation rate reaching 1.26 kg/m2/h under one sun irradiation, and maintained excellent performance through cyclic operations.
8. Xing D, Chang C, Xi XY, Hao B, Zheng Q*, Gutnikov SI, Lazoryak BI, Ma PC*. Morphologies and mechanical properties of basalt fibre processed at elevated temperature. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 2022, 582, 121439. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2022.121439.

■ Basalt fiber (BF) morphologies and properties following annealing at different temperatures in an air atmosphere are reported. The heat treatment caused the formation of crystals on the fiber surface, which altered BF from the paramagnetic material to the ferromagnetic one. The tensile strength of BF was reduced significantly upon thermal treatment.
9. Li M, Xing D, Zheng Q, Li H, Hao B, Ma PC*. Corrosion behaviors of basalt fiber exposed to acids. Construction and Building Materials, 2022, 316, 125783. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.125783.
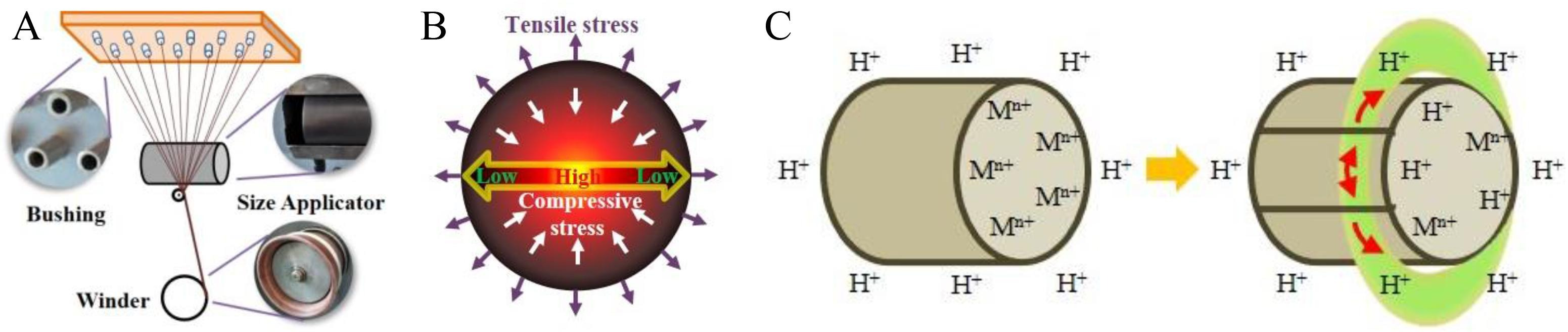
■ The corrosion behaviors of basalt fiber (BF) exposed to three typical acids, HCl, H2SO4, and HNO3 solutions, were thoroughly investigated. Employing an orthogonal array design via the Taguchi method, the study elucidated the relationship between BF’s tensile strength and experimental conditions, including acid concentration, immersion temperature, and time.
10. Li M, Xing D, Zheng Q, Li H*, Hao B, Ma PC*. Variation on the morphology and tensile strength of basalt fiber processed in alkali solutions. Construction and Building Materials, 2022, 335, 127512. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2022.127512.

■ Basalt fiber (BF) degradation behaviors are reported when exposed to NaOH, KOH, and Ca(OH)2 solutions, employing the Taguchi method with orthogonal arrays. The comprehensive analysis explores the overall impacts of alkali type, concentration, immersion temperature, and time on the tensile strength of BF.
11. Zhai HP, Xing D, Liang CG, Hao B, Yue X, Ma PC*. Formula development of sizing for basalt fiber. Part I: Role of film former. The Journal of The Textile Institute, 2022, 114, 1366-1374.
https://doi.org/10.1080/00405000.2022.2124656.
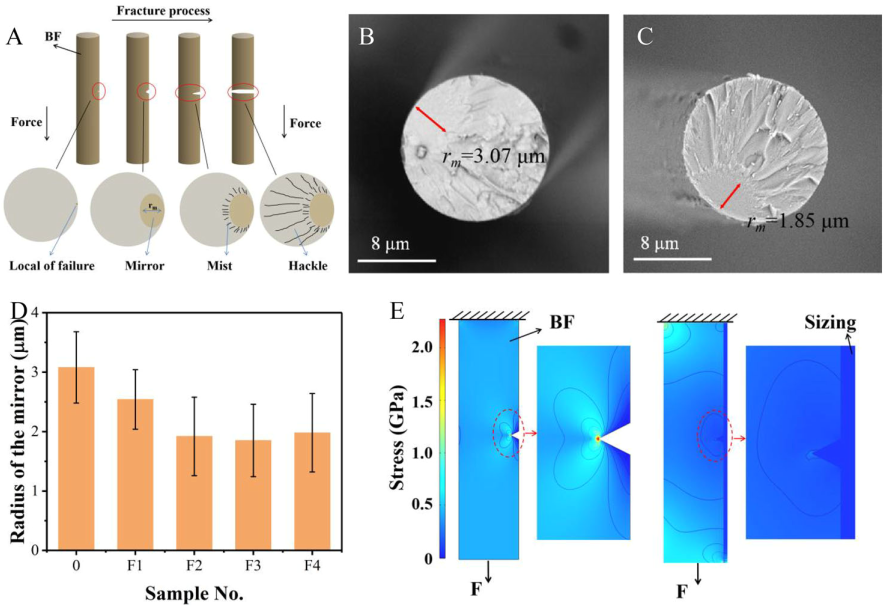
■ Sizing with different components and concentrations was formulated using the Taguchi method with an orthogonal array design, aiming to optimize the formulation of BF sizing. Based on the optimized result, we specifically studied the effect of film former and its content on the mechanical properties of BF and the role of film former in governing the overall performance of sizing was illustrated.
12. Sun HB, Xing D*, Liang CG, Hao B, Yue X, Ma PC*. Development of fluorescent basalt fiber with nanocomposite sizing for acid indication and anti-counterfeiting. Composites Communications, 2022, 35, 101291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coco.2022.101291.
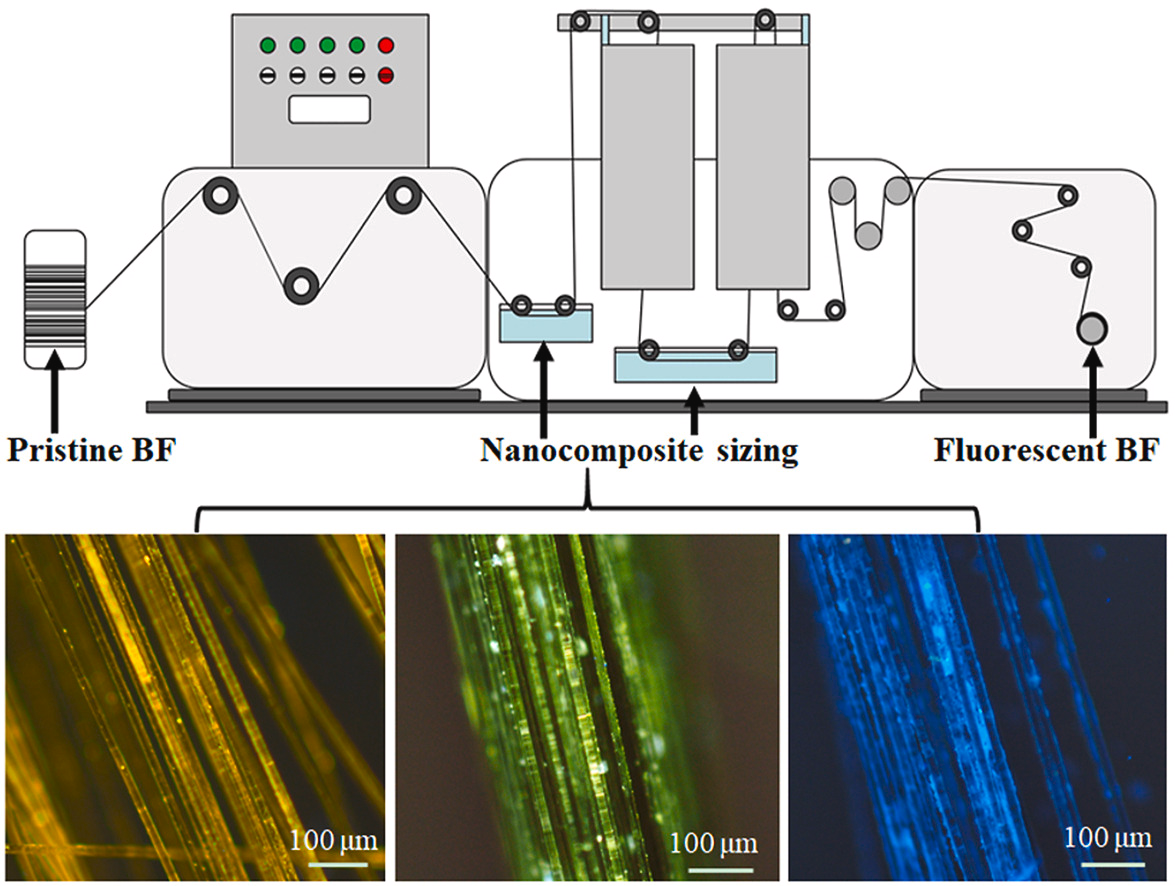
■ To produce fluorescent basalt fiber (BF) by applying nanocomposite sizing to the fiber surface is reported. This approach yielded filaments with exceptional fluorescent properties, customizable colors, heightened sensitivity to H+, and robust anti-counterfeiting capabilities. Moreover, the mechanical strength of BF was markedly enhanced post-sizing, attributed to defect repair and improved filament bonding.
13. Guo ZS, Xing D, Xi XY, Yue X, Liang CG, Hao B, Zheng Q, Gutnikov SI, Lazoryak BI, Ma PC*. Production of fibres from lunar soil: Feasibility, applicability, and future perspectives. Advanced Fiber Materials, 2022, 4, 923–937. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42765-022-00156-5.
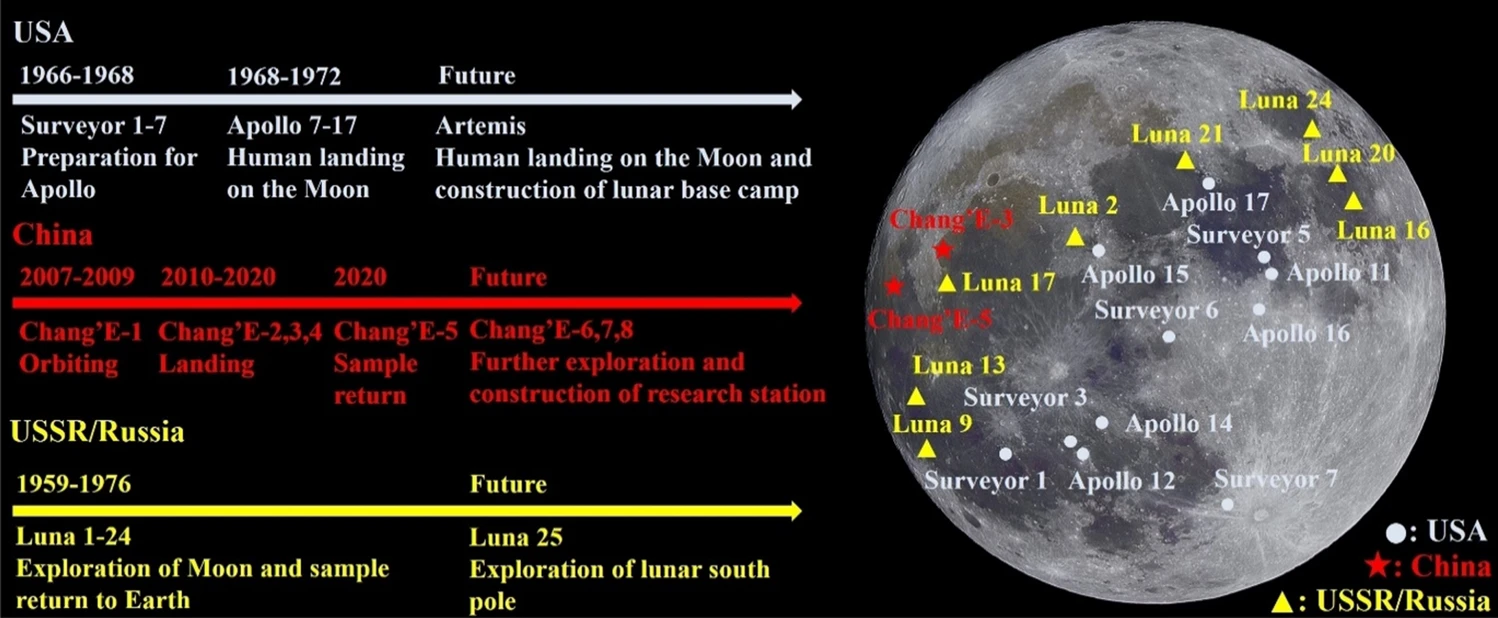
■ Recent advancements in converting lunar soil simulants into model lunar soil fibers have been summarized, along with insights into their potential application for producing actual lunar soil fibers on the Moon, which are crucial for lunar base construction. Achieving in-situ resource utilization of lunar soil poses significant challenges, necessitating further contributions from both scientific and engineering communities to advance the field.
14. Song D, Kadier A, Peralta-Hernandez JM, Xie H*, Hao B, Ma PC*. Separation of oil-water emulsions by a novel packed bed electrocoagulation (EC) process using anode from recycled aluminum beverage cans. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2022, 379, 134693. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.134693.
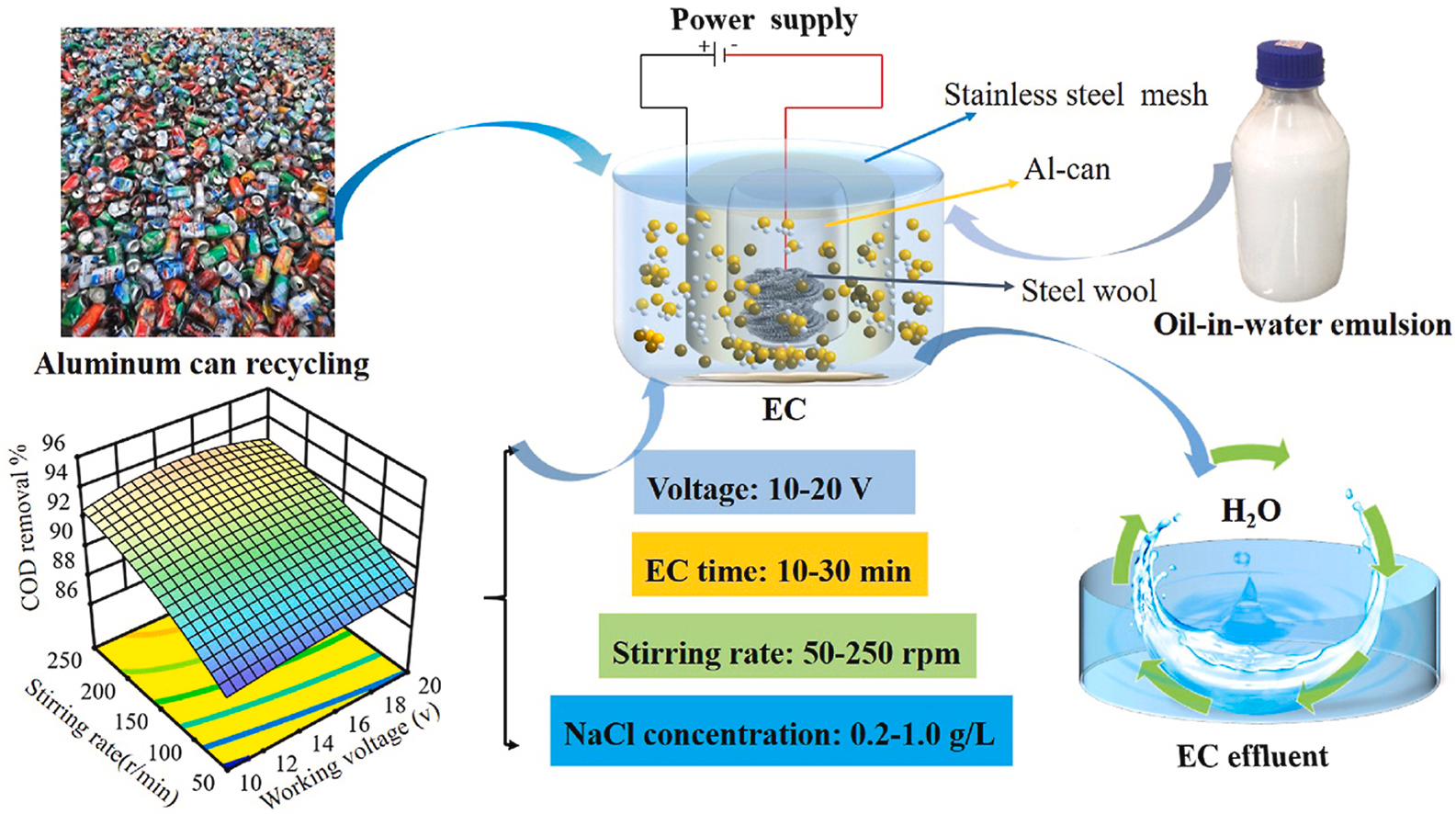
■ Evaluation of an electrocoagulation (EC) reactor utilizing recycled aluminum cans filled with steel wool as anode and commercial stainless-steel mesh as cathode for oil-water emulsion separation was conducted. Response Surface Methodology (RSM) optimization yielded over 93% oil removal efficiency under ideal conditions: EC process time of 10 min, applied voltage of 15 V, stirring rate of 250 rpm, and NaCl concentration of 1 g/L.
15. Kadier, A*, Singh, R, Song, D, Ghanbari, F, Zaidi, NS, Prihartini PT, Jadhav, DA, Islam, MA, Kalil, MS, Nabgan, W*, Abdul HA, Hasan, HA, Ma, PC*. A novel pico-hydro power (PHP)-microbial electrolysis cell (MEC) coupled system for sustainable hydrogen production during palm oil mill effluent (POME) wastewater treatment. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2023, 48, 21066–21087. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2022.09.023.
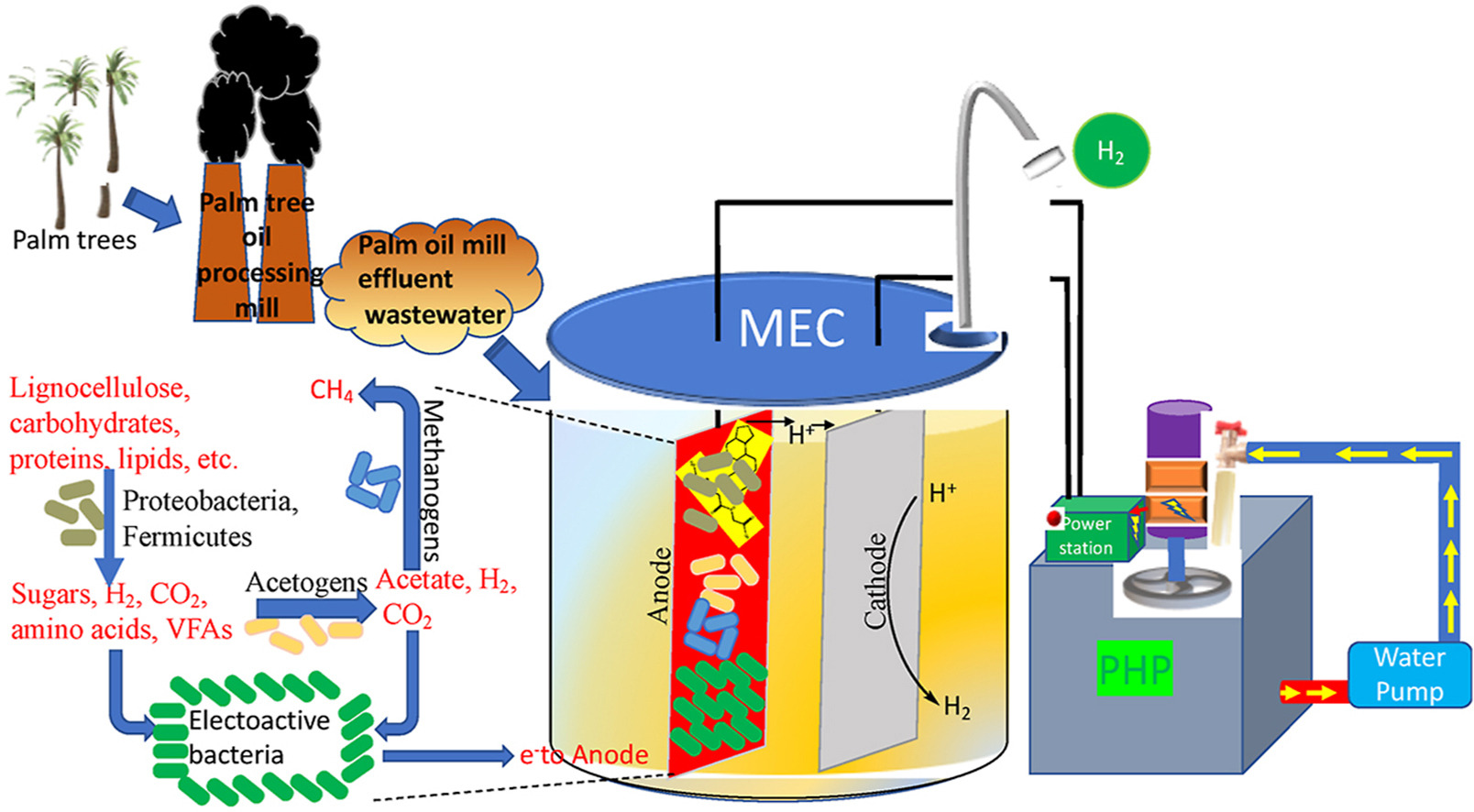
■ A stable hydropower-based system is reported to energize Microbial Electrochemical Cells (MECs) treating POME wastewater, enhancing performance, and addressing energy-related challenges. Integrating a PHP generator with MECs shows promise in significantly improving MEC performance and converting wastewater into a cleaner fuel source. Insights provided guide the design of efficient PHP-MEC models for various industrial effluents and offer solutions to common MEC issues.
16. Othmani, A, Kadier, A*, Singh, R, Igwegbe, C.A, Bouzid, M, Aquatar, MO, Khanday, WA, Bote, ME, Damiri, F, Gokkus, O, Sher, F*. A comprehensive review on green perspectives of electrocoagulation integrated with advanced processes for effective pollutants removal from water environment. Environmental Research, 2022, 215, 114294. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2022.114294.
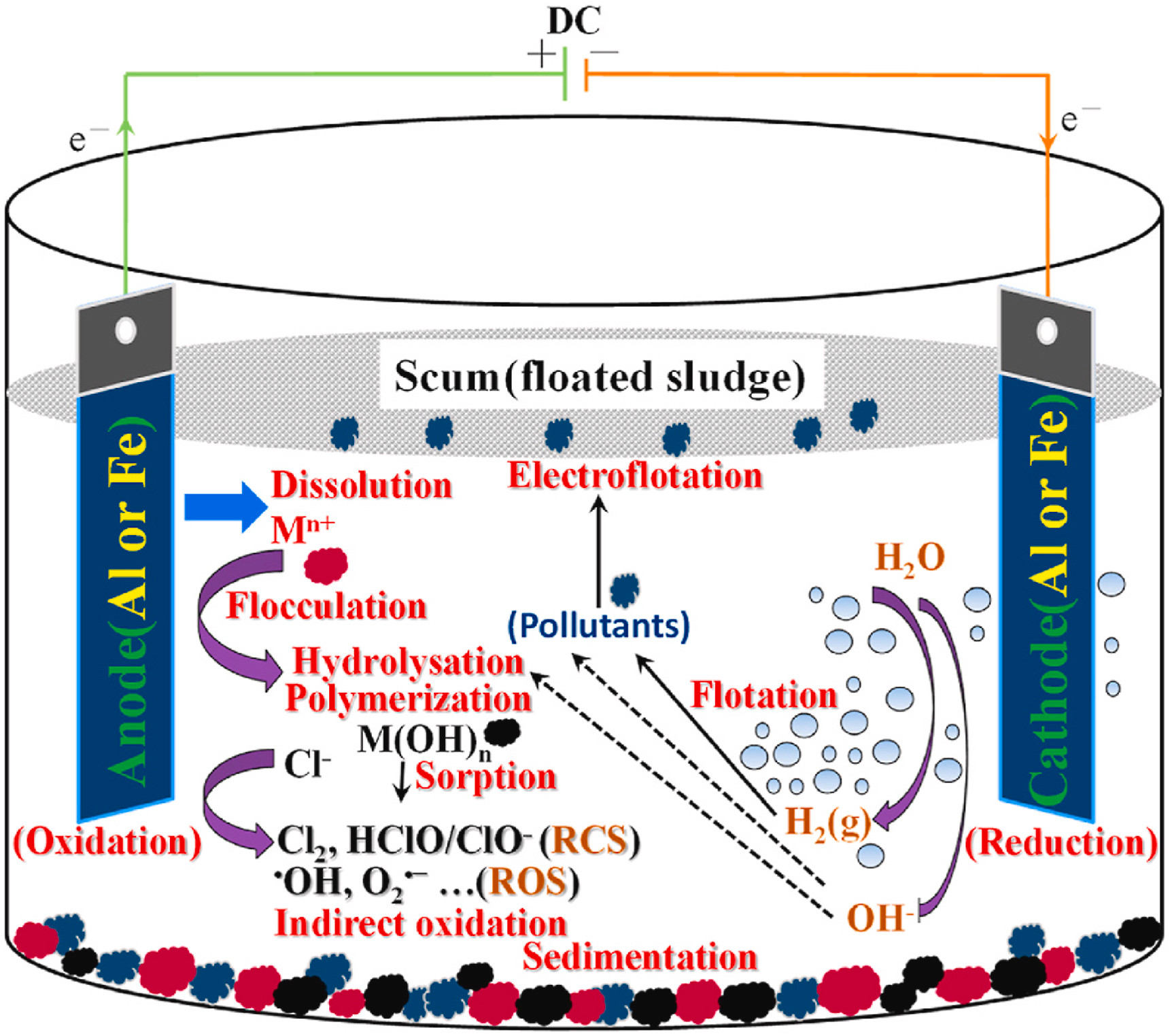
■ A comprehensive review of 20 years of literature on electrocoagulation (EC), focusing on fundamentals, reactor design, implementation, and performance enhancement through coupling with various treatment processes, is reported. The study discusses achievements, future potential, and challenges in modeling future EC-integrated systems for wastewater purification.
17. Nidheesh PV*, Khan FM, Kadier A, Akansha J, Bote ME, Mousazadeh M. Removal of nutrients and other emerging inorganic contaminants from water and wastewater by electrocoagulation process. Chemosphere, 2022, 307, 135756. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.135756.
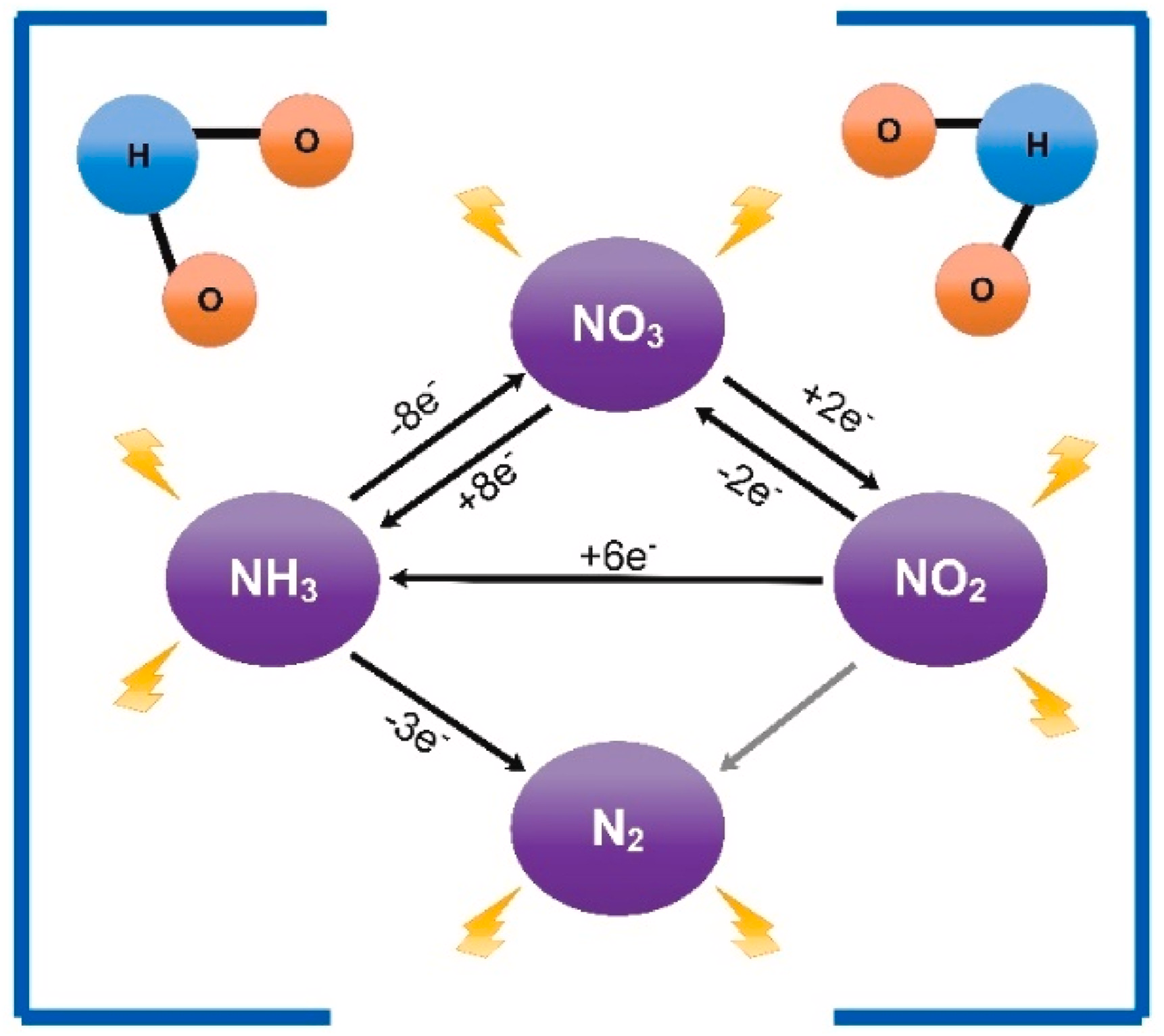
■ The use of EC technology to remove nutrients and other emerging inorganic pollutants from water medium is reported. The operating factors that influence EC process efficiency are explained. The major advancement of the EC technique and field-implemented units are also discussed.
18. Villasenor-Basulto DL, Kadier A, Singh R, Navarro-Mendoza R, Bandala E, Peralta-Hernandez JM*. Post-tanning wastewater treatment using electrocoagulation: Optimization kinetics and settlement analysis. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2022, 165, 872–886. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2022.08.008.
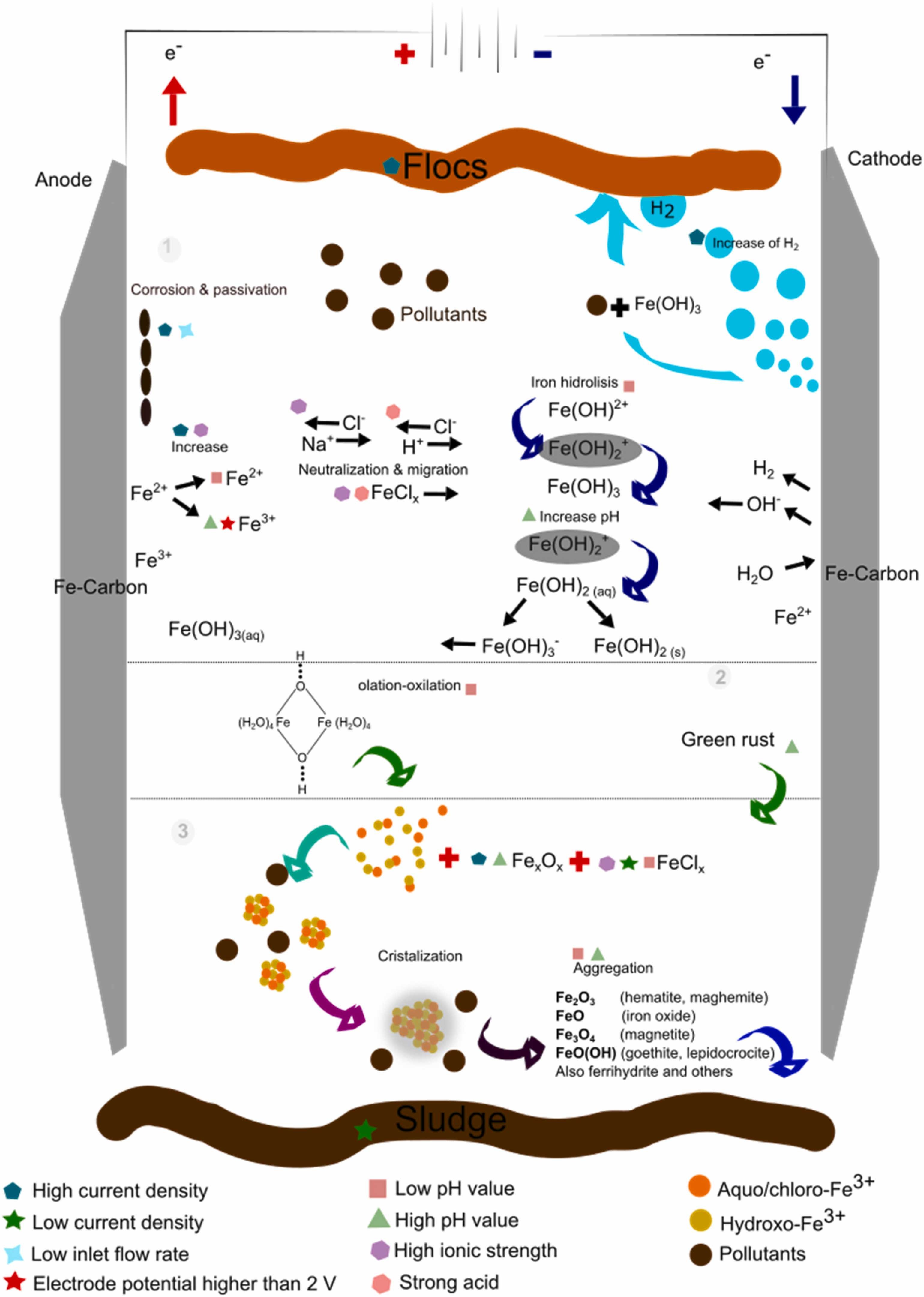
■ Statistical analysis was used to explain coagulant-flocculant elements generated by steel-carbon electrodes operated under different conditions. Kinetics analysis was used to determine the reaction rate, the amount of dye adsorbed by the produced iron complexes, and the rate-limiting process. Also, sludge morphology was analyzed to observe the differences due to different parameter values. Based on statistically optimized results, a pre-pilot run with post-tanning real wastewater treatment was constructed.
19. Saratale GD, Banu JR, Nastro RA, Kadier A, Ashokkumar V, Lay CH, Jung JH, Shin HS, Saratale RG, Chandrasekhar K*. Bioelectrochemical systems in aid of sustainable biorefineries for the production of value-added products and resource recovery from wastewater: A critical review and future perspectives. Bioresource Technology, 2022, 359, 127435. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2022.127435.
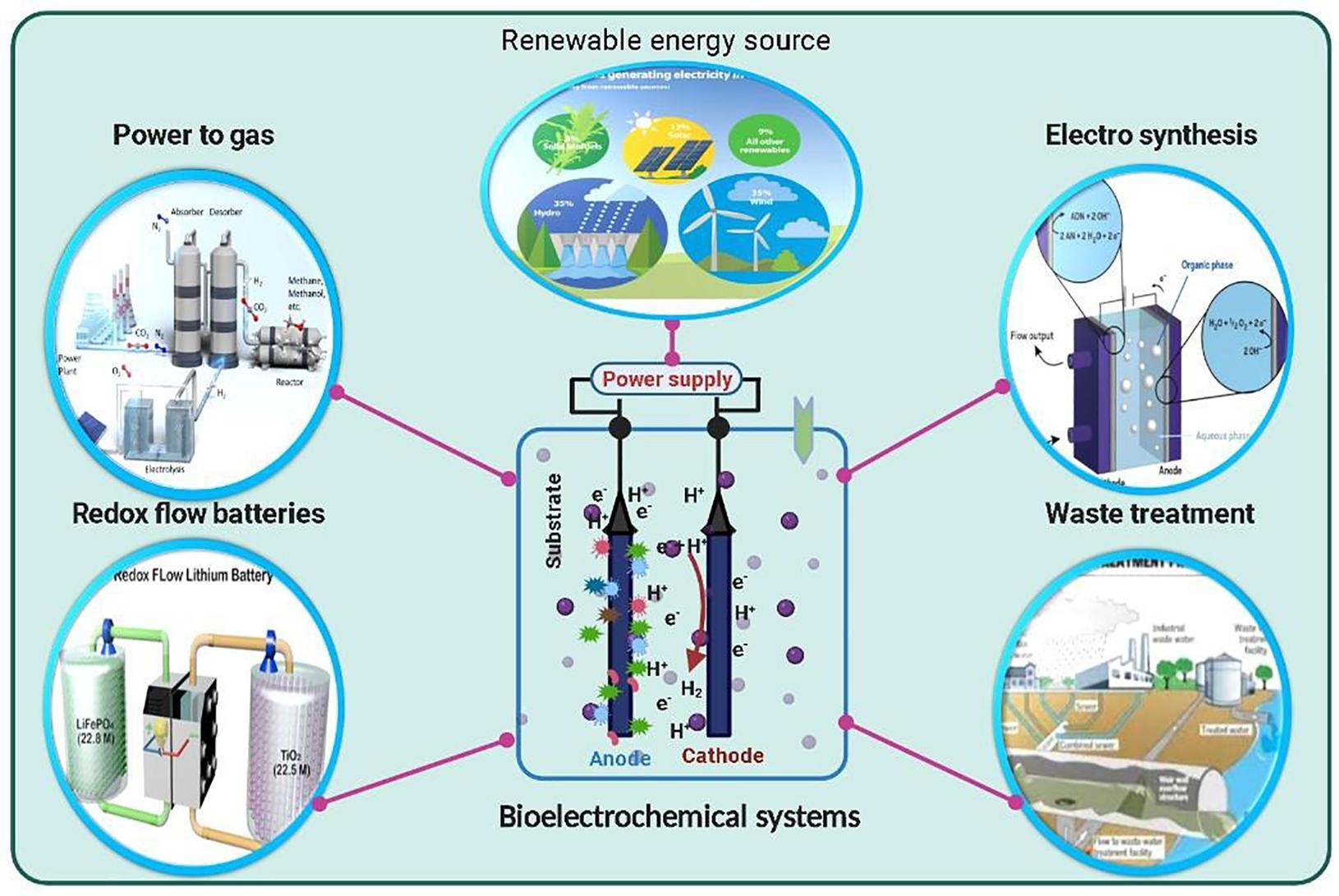
■ The potential of Bioelectrochemical Systems (BES) for diverse applications, including waste biorefinery, pollutant removal, CO2 capture, and clean biofuel electrosynthesis, is reviewed. It highlights recent advancements and innovative results from BES research, focusing on hybrid approaches for product recovery and wastewater treatment and detailed insights into waste biorefinery designs.
20. Bahrodin MB, Zaidi NS*, Kadier A, Hussein N, Syafiuddin A, Boopathy R*. A novel natural active coagulant agent extracted from the sugarcane bagasse for wastewater treatment. Applied Sciences, 2022, 12, 7972. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12167972.
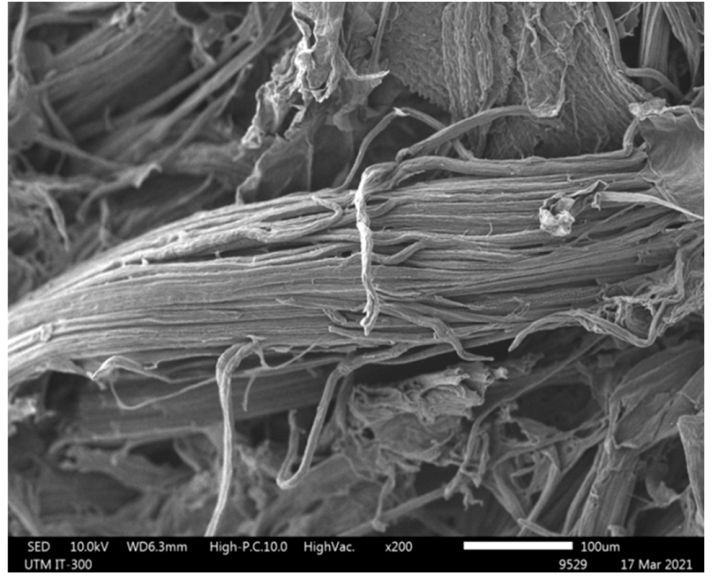

■ To analyze the effect of the extraction process in optimizing the active coagulant agent of bagasse as a natural coagulant for optimum turbidity removal is reported. Bagasse was characterized in terms of physical, chemical, and morphological properties. The results showed that bagasse has a very high polysaccharide content, which can act as an active coagulant agent with hemicellulose and lignin.
21. Leng X, Tegladza ID, Kadier A, Dai H, Lu J*. In-situ generation of both hydroxyl radical and adsorptive flocs in electrocoagulation process with air breathing cathode. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2022, 164, 345–353. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2022.06.015.
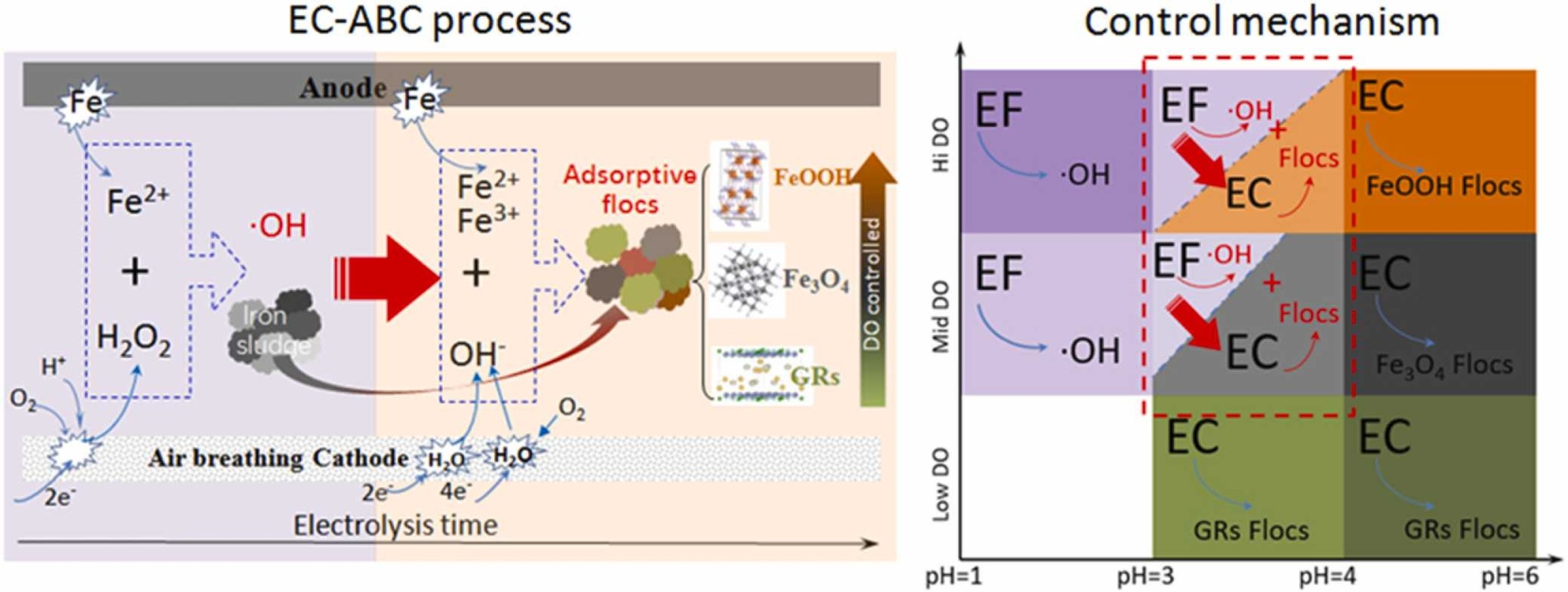
■ Combining electrocoagulation (EC) and electro-Fenton for water treatment, an EC process with an air-breathing cathode was developed to simultaneously generate hydroxyl radicals and adsorptive flocs in a single cell. The effectiveness of carbon-based porous cathode materials, carbon fiber, and granular activated carbon was compared with traditional Fe plate cathodes. The study also focused on the factors influencing the formation of radicals and flocs, such as dissolved oxygen, pH, cathode material, and electrolysis time.
22. Aryanti PT*, Nugroho FA, Prabowo BH, Prasetyo T, Rahayu FS, Kadier A, Sher F. Integrated electrocoagulation-tight ultrafiltration for river water decontamination: The influence of electrode configuration and operating pressure. Cleaner Engineering and Technology, 2022, 9, 100524. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clet.2022.100524.

■ The treatment of contaminated river water was advanced by integrating tight ultrafiltration (tight-UF) membranes, achieving high-quality water standards. With a molecular weight cut-off close to nanofiltration, this membrane showed superior selectivity for removing soluble contaminants over conventional UF methods. Operational conditions were optimized for maximum contaminant rejection, including electrode configuration, applied current in the EC process, and operating pressure for the tight UF.
23. Zaidi NS, Syafiuddin A, Sillanpää M, Bahrodin MB, Zhang Zhan L, Ratnasari A, Kadier A, Mehmood MA, Boopathy R*. Insights into the potential application of magnetic field in controlling sludge bulking and foaming: A review. Bioresource Technology, 2022, 358, 127416. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2022.127416.
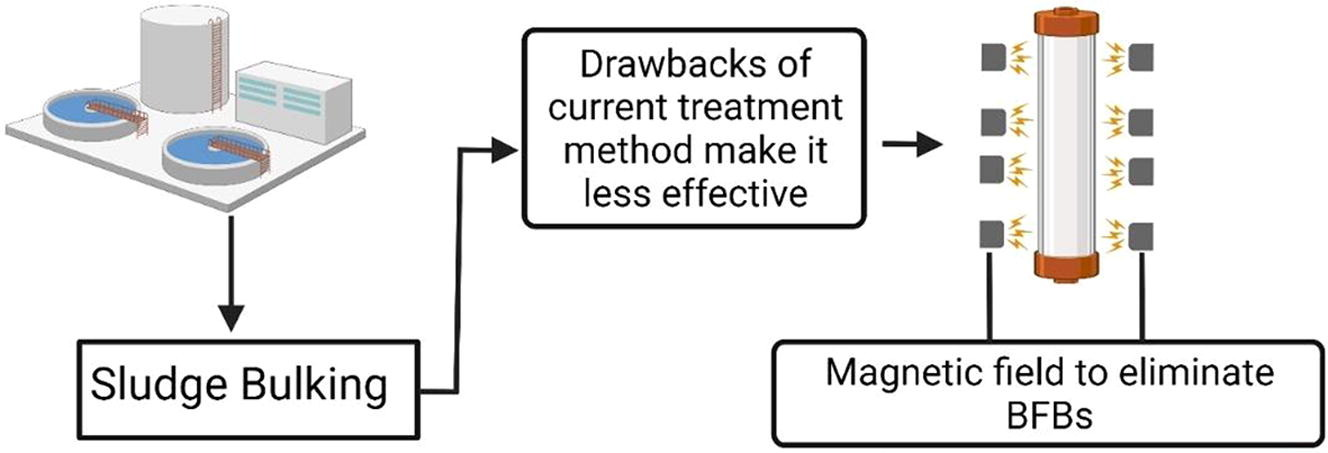
■ Essential parameters influencing bulking and foaming bacteria growth are comprehensively summarized, alongside a critical review of existing control approaches, highlighting their drawbacks and limitations. This review underscores the potential of magnetic fields in preventing bulking and foaming bacteria proliferation, pointing toward future research directions.
24. Moussavi SP, Kadier A*, Singh R, Ashoori R, Shirinkar M, Lu J, Zaidi NS, Sher F*. Superior removal of humic acid from aqueous stream using novel calf bones charcoal nanoadsorbent in a reversible process. Chemosphere, 2022, 301, 134673. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.134673.
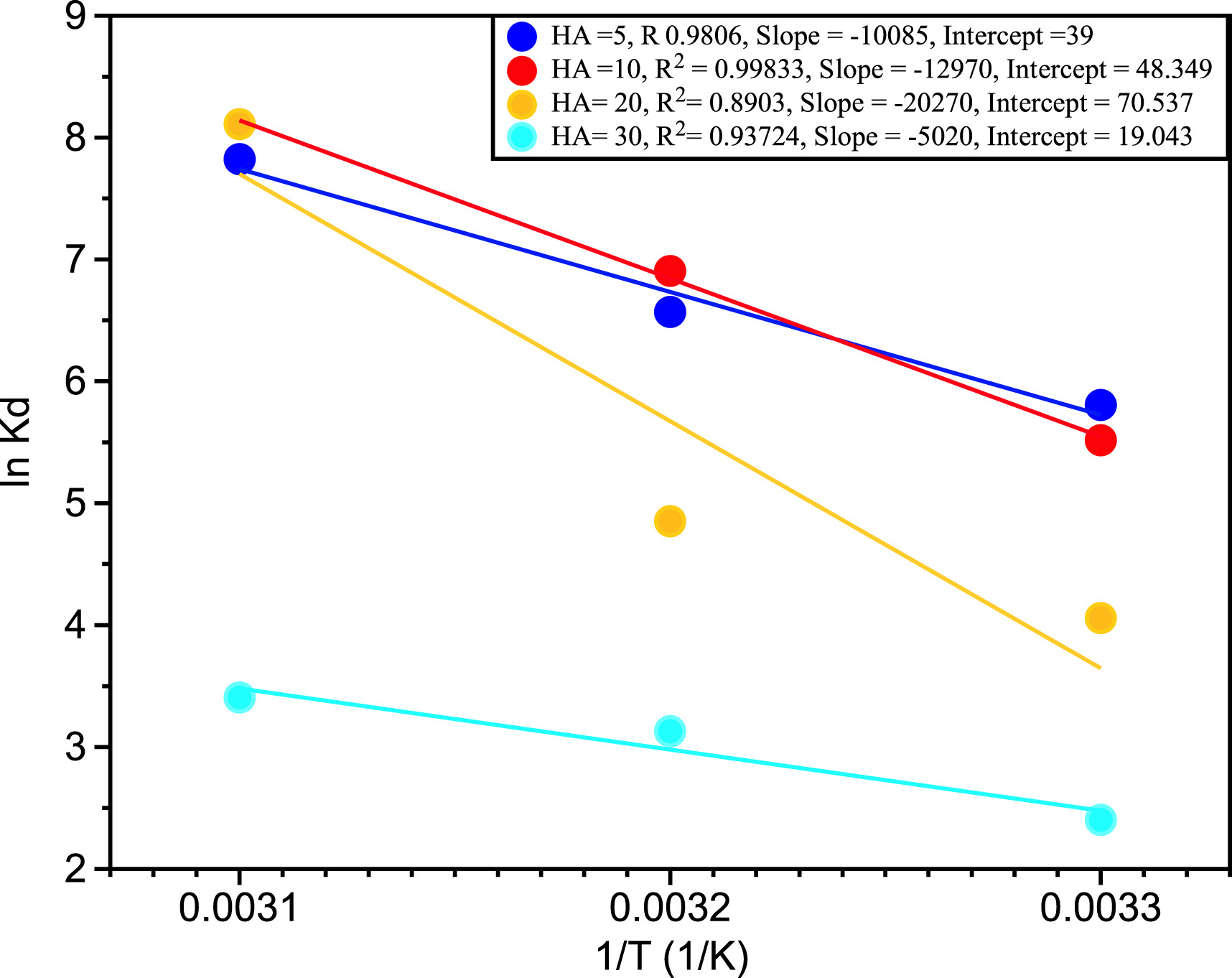
■ A robust CBC-based process for humic acid (HA) removal is optimized, utilizing kinetic models to elucidate CBC’s high adsorption efficiency and demonstrating sustainability through the regeneration of exhausted CBC. Supported by kinetic models, these optimizations provide a statistical framework for process characterization, aiming to guide the design of large-scale water pre-treatment plants for HA-free potable water and offering a theoretical basis for removing similar pollutants.
25. Kashani MRK, Kiani R, Hassani A, Kadier A*, Madihi-Bidgoli S, Lin KYA, Ghanbari F*. Electro-peroxone application for ciprofloxacin degradation in aqueous solution using sacrificial iron anode: A new hybrid process. Separation and Purification Technology, 2022, 292, 121026. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2022.121026.
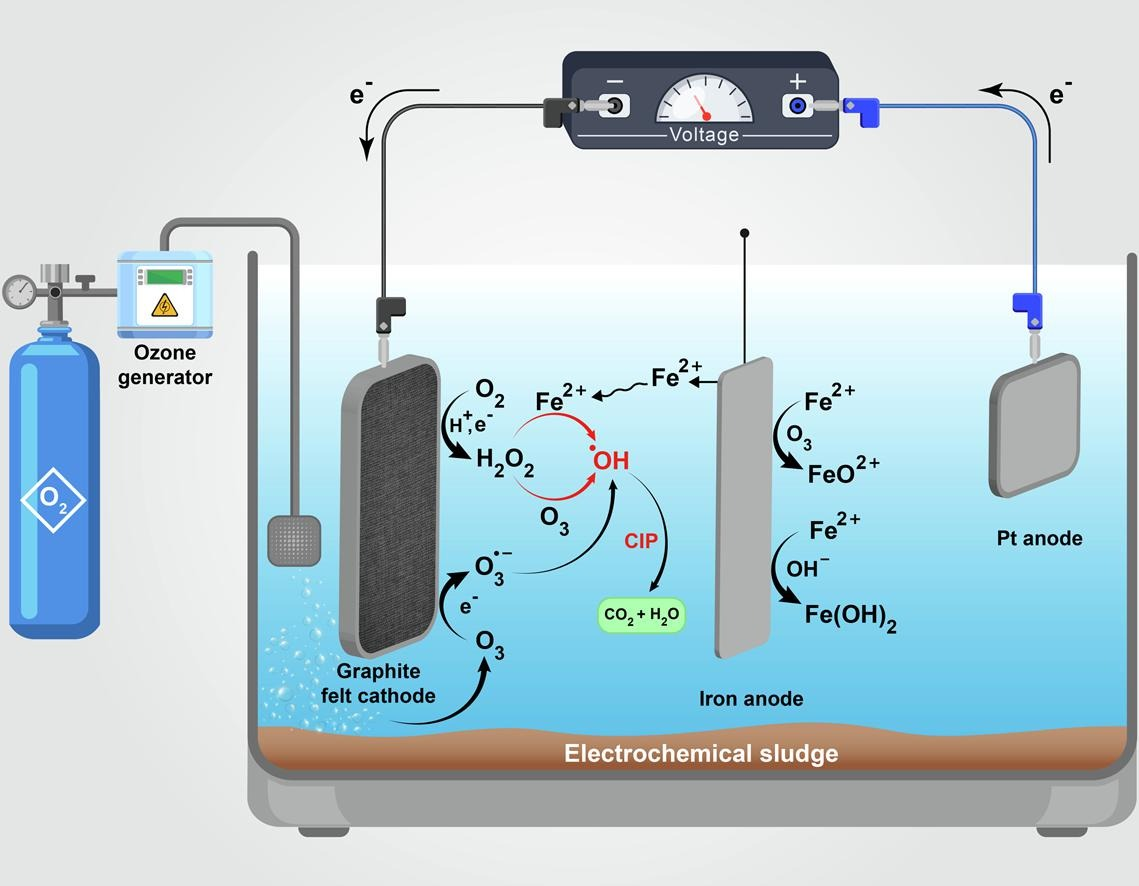
■ The EP process, enhanced by an additional iron anode for CIP degradation or coagulation, was examined. Operational factors were evaluated, including solution pH, applied current, and ozone dosage on CIP removal. The study assessed various process configurations to elucidate each system’s role and mechanism. The effectiveness of the EP/iron process was tested on hospital effluent, serving as a real matrix evaluation.
26. Loh ZZ, Zaidi NS, Yong EL*, Syafiuddin A*, Boopathy R, Kadier A. Current status and future research trends of biofiltration in wastewater treatment: A bibliometric review. Current Pollution Reports, 2022, 8, 234–248. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40726-022-00224-9.

■ Biofiltration in wastewater treatment’s progress and future directions were reviewed through bibliometric analysis, offering a distinct approach by analyzing the field’s development rather than providing a comprehensive overview. This analysis included trends in annual publications, key journals, leading contributors, countries, affiliations, prevalent keywords, and the varieties of wastewater treated, delivering unique insights into the impact and growth of biofiltration technology in environmental protection.
27. Ting WC, Zaidi NS*, Loh ZZ, Bahrodin MB, Awang NA, Kadier A. Assessment and optimization of a natural coagulant (Musa paradisiaca) peels for domestic wastewater treatment. Environmental and Toxicology Management, 2022, 2, 7-13. https://doi.org/10.33086/etm.v2i1.2901.
■ Domestic wastewater treatment using banana peels as a natural coagulant was explored, characterizing the peels based on physical, chemical, and morphological properties. The effects of pH, dosage, and agitation speed on the removal performance were investigated, optimizing the use of banana peels for efficient wastewater treatment.
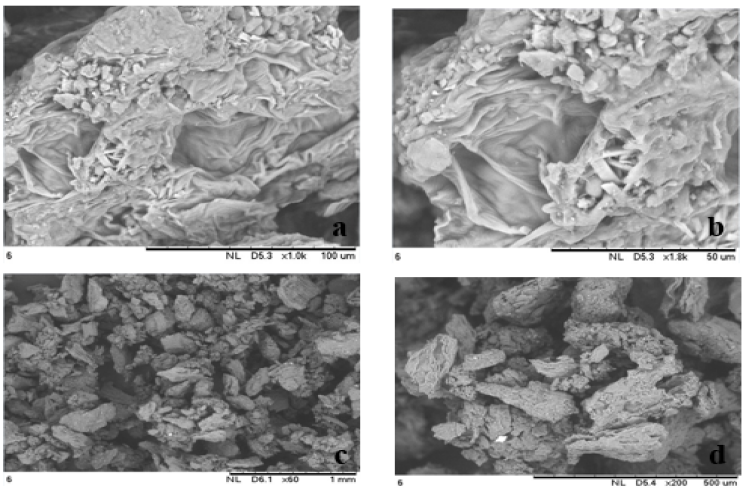
28. Wang JY, Kadier A*, Hao B, Li H, Ma PC*. Performance optimization of a batch scale electrocoagulation process using stainless steel mesh (304) cathode for the separation of oil-in-water emulsion. Chemical Engineering & Processing: Process Intensification, 2022, 174, 108901. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cep.2022.108901.
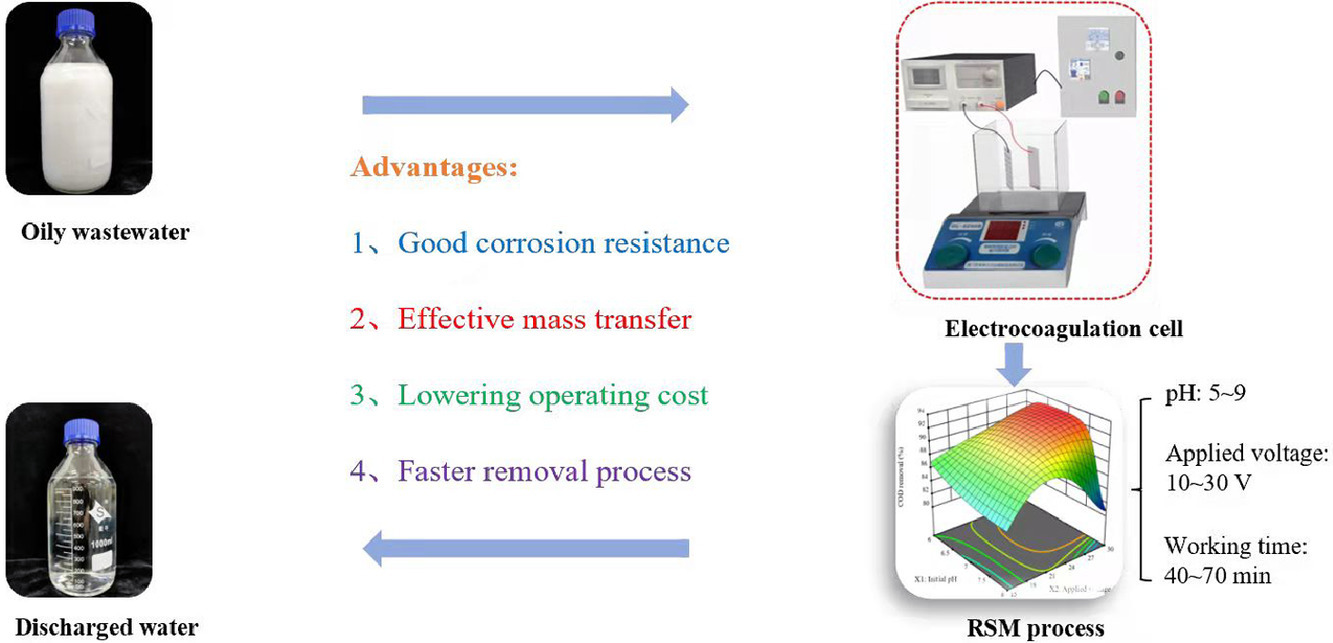
■ A commercially available stainless-steel mesh was used as a cathode for its corrosion resistance and conductivity, significantly lowering operational costs. Employing response surface methodology for an aluminum plate-stainless steel mesh electrode combination, an optimal oil removal efficiency of 90.86% was achieved at pH=7.0, 25V, and 60 minutes, with sludge analysis conducted via SEM/EDS and ATR-FTIR spectroscopy.
29. Kadier A*, Wang J, Chandrasekhar K, Abdeshahian P, Islam MA, Ghanbari F*, Bajpai M, Katoch SS, Bhagawati PB, Li H*, Kalil MS, Hamid AA, Hasan HA, Ma PC*. Performance optimization of microbial electrolysis cell (MEC) for palm oil mill effluent (POME) wastewater treatment and sustainable Bio-H2 production using response surface methodology (RSM). International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2022, 47, 15464-15479. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2021.09.259.
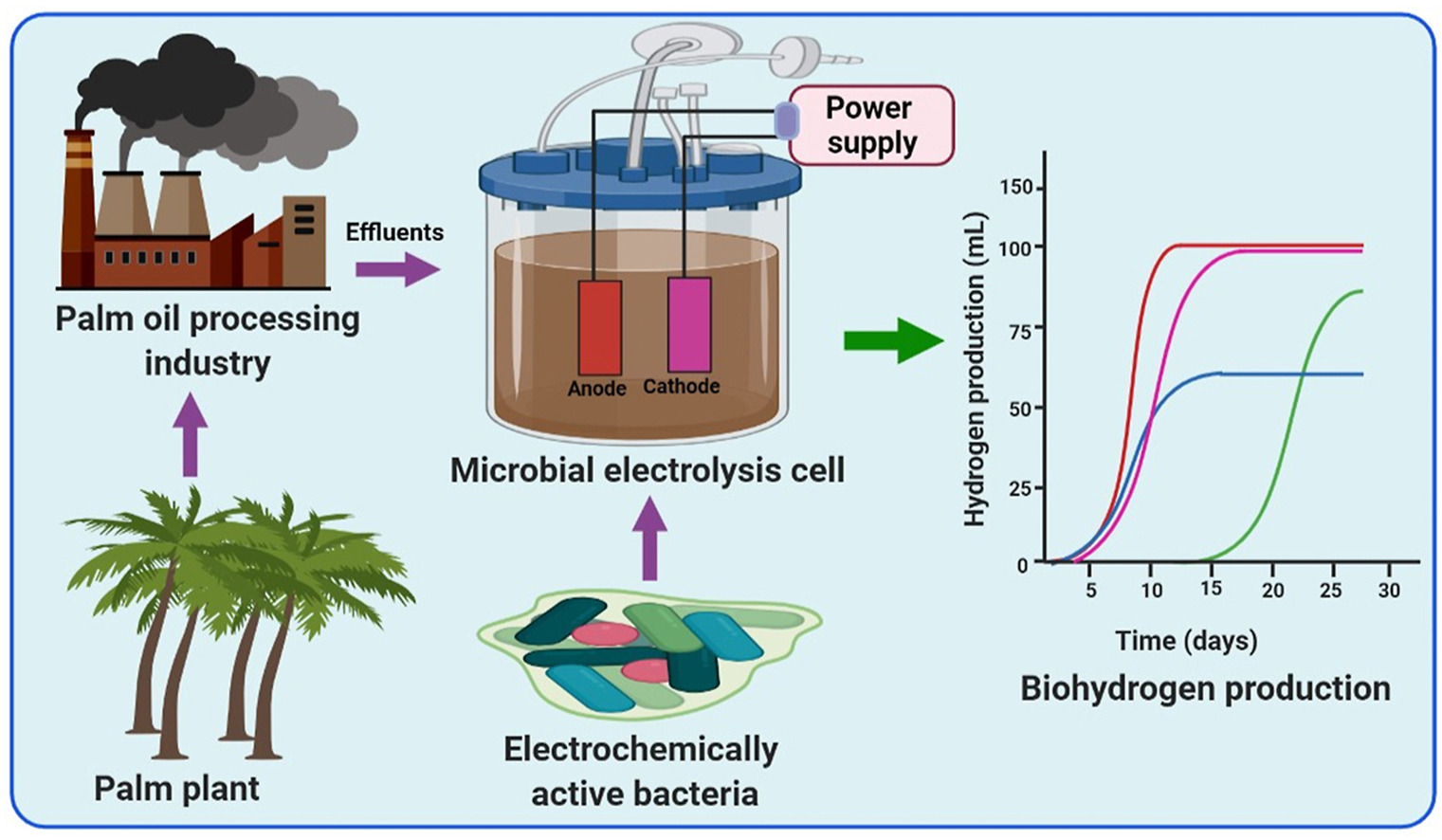
■ Palm oil mill effluent for H2 production via the microbial electrochemical cell method as a viable treatment approach is reported. To optimize H2 generation, an empirical model was developed using response surface methodology. A central composite design with twenty experimental runs was employed, considering crucial variables, including incubation temperature, initial pH, and influent dilution rate.
30. Dandan Ouyang, Chunyan Wang, Hui Zhu, Feng Yu*, Jiao Yin*, Bismuth nanoparticles encapsulated in mesoporous carbon nanofibers for efficient potassium-ion storage, ACS Applied Nano Materials, 2022, 5, 9, 13171–13179. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsanm.2c02918
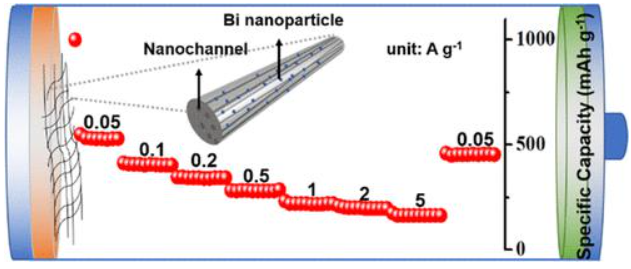
■ Bi nanoparticles encapsulated in mesoporous carbon nanofibers (Bi/PCNFs) were fabricated via simple electrospinning. Benefiting from the carbon coating structure, ultrafine Bi nanoparticles (5 nm), and plentiful vessel-like mesopores, the Bi/PCNFs electrodes show an excellent reversible capacity and ultralong cycle stability.
31. Nan Xue, Yue Zhang, Chunyan Wang, Xueyan Xue, Dandan Ouyang, Hui Zhu*, Jiao Yin*, Enhancing oxygen reduction reaction performance in acidic media via bimetal Fe and Cr synergistic effects, Int. J. Hydrog. Energy, 2022, 47, 33979-33987.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2022.07.266.
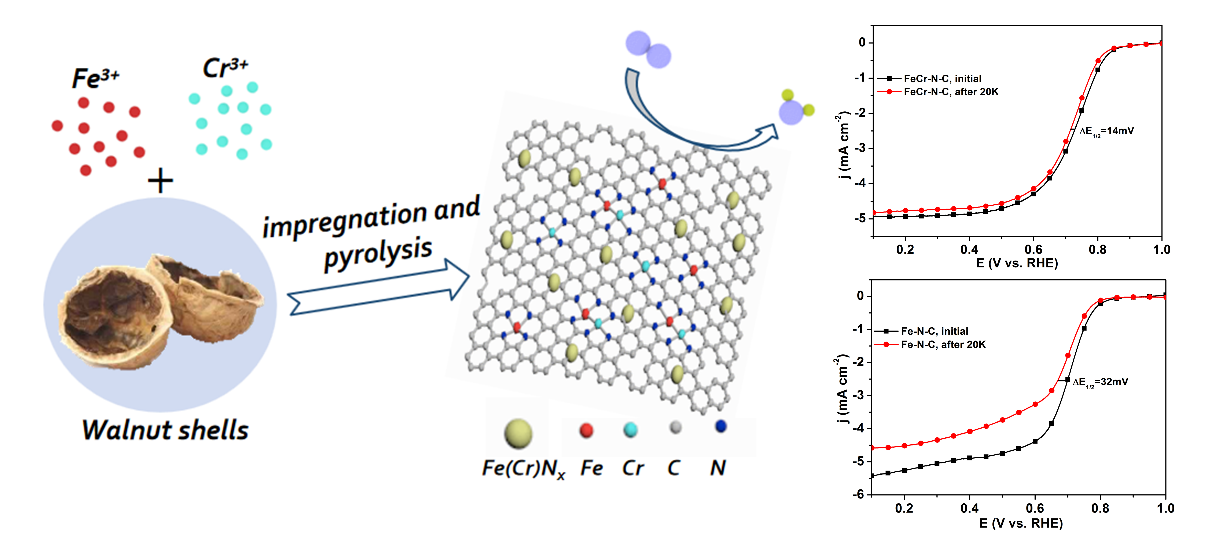
■ The synergistic effect of Fe and Cr inhibits Fenton reaction and improves the ORR activity and long-term durability of the catalyst in acidic media.
附件下载: