2021
1. Zhang YR, Meng BW, Hao B, Ma PC*. Aggregation-induced demulsification triggered by the hydrophilic fabric for the separation of highly emulsified oil droplets from water. Aggregate, 2022, 3, e131. https://doi.org/10.1002/agt2.131.
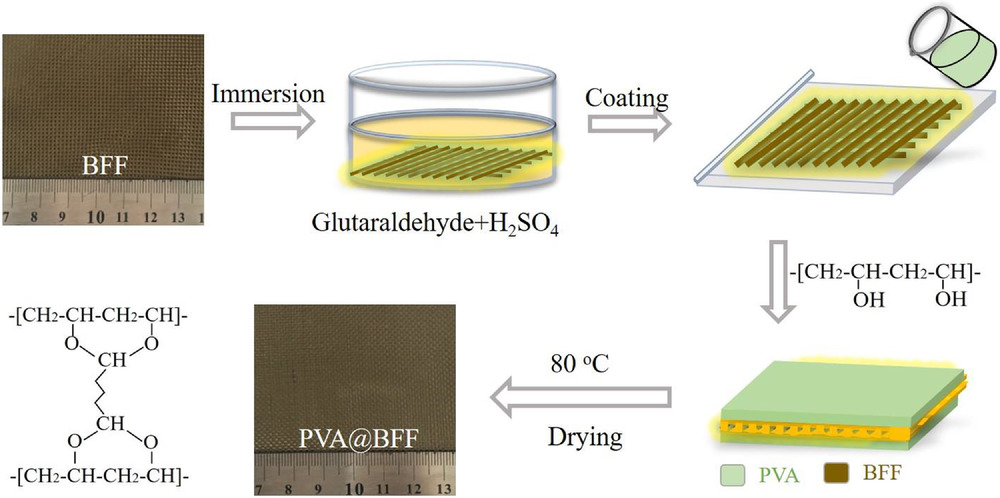
■ A functional fabric with a basalt fiber substrate and a polyvinyl alcohol coating was developed to effectively separate highly emulsified oil from water. The coating’s hydrophilicity and the fabric’s microchannels synergistically increase oil concentration, facilitating droplet aggregation and separation. This process, termed aggregation-induced demulsification, was confirmed by analyzing oil droplet distribution in emulsions, offering a cost-effective, high-performance separation solution.
2. Zhang L, Yasin A*, Li M, Hao B, Ma PC*. Silicate based solar evaporator with self-cleaning and corrosion resistant properties for durable seawater desalination. Sustainable Materials and Technologies, 2021, 30, e00362. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.susmat.2021.e00362.

■ A solar evaporator featuring a polypyrrole-modified commercial sand core and basalt fiber within a silicate-based structure was developed for efficient solar steam generation. This design ensures mechanical strength and stability in seawater, highlighting its potential for continuous operation. Achieving an 85.9% evaporation efficiency and a 1.26 kg/m2/h rate under one sun irradiation, the evaporator also excels in cyclic performance.
3. Li M, Hao B, Zhang L, Li H, Lv P, Yue X, Yasin A, Ma PC*. Facile preparation of a polysilsesquioxane sheet with a three-dimensional structure. Materials Chemistry Frontiers, 2021, 5, 7176-7183. https://doi.org/10.1039/d1qm00785h.
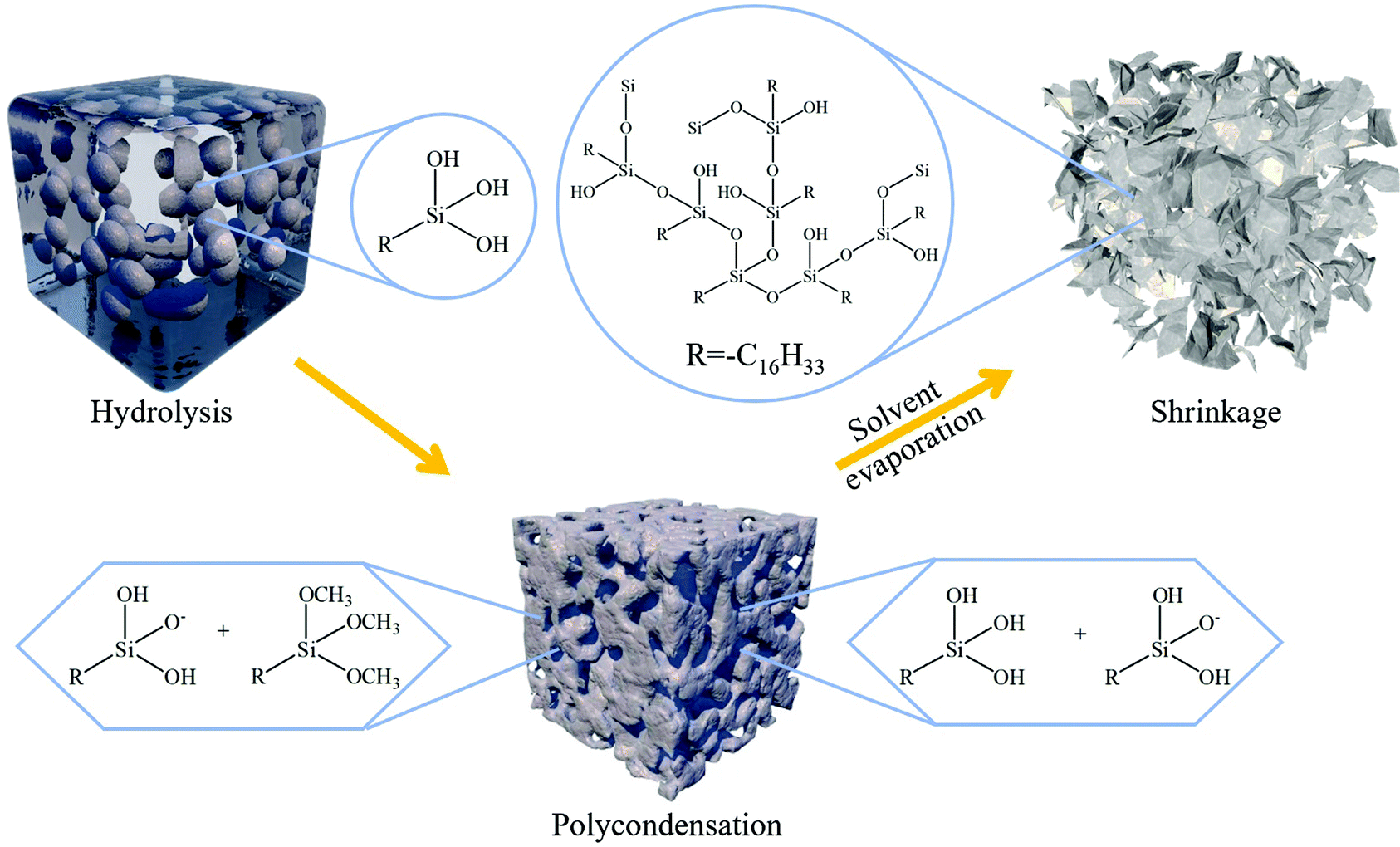
■ A novel porous silsesquioxane (PSQ) with a 3-D interconnected structure was synthesized via the hydrolysis of hexadecyltrimethoxysilane (HDTMS). The influence of reaction parameters on PSQ morphology was explored, with the growth of the network structure monitored by SEM throughout the reaction process. The formation mechanism involved the collision and condensation of hydrolyzed silanes into a 3-D network.
4. Xing D, Xi XY, Qi MG, Zheng QB, Ma PC*. Optimization on the formulation of sizing to enhance the mechanical properties of basalt fiber. The Journal of The Textile Institute, 2020, 4, 515-525. https://doi.org/10.1080/00405000.2020.1771078.
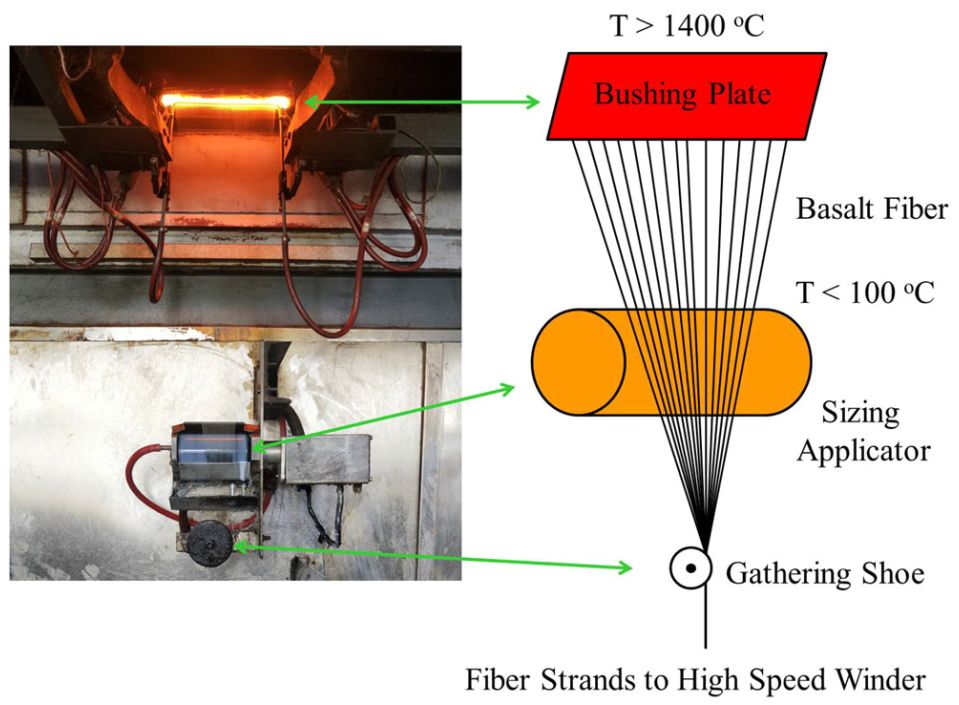
■ Sizing formulations with varying components and concentrations were optimized using the Taguchi method and orthogonal array design, targeting basalt fiber mechanical performance enhancement. The effectiveness of the optimized formulation in improving BF’s mechanical properties was confirmed. Additionally, the study explored factors influencing the sizing’s spreadability and interaction with the fiber by examining surface tension and adhesive forces, providing insights into the mechanics of fiber treatment.
5. Meng BW, Yue X, Zhang YR, Yang FH, Xing D, Ma PC*. Direct visualization of interfacial debonding in FRP structure using an AIE molecule. Composites Communications, 2021, 27, 100816. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coco.2021.100816.

■ A method using TPE-4N with aggregation-induced emission was developed to detect interfacial debonding in FRPs. The method translates invisible strain into a quantifiable fluorescence signal by dip-coating basalt fibers with TPE-4N and embedding them in polydimethylsiloxane. This technique revealed a debonding strain of 5.25%, lower than the 6.93% found by traditional methods, proving its efficacy for direct damage visualization in FRP structures.
6. Jiang F, Wang X, Fan X, Zhu H*, Yin J*. Oxygen-functionalized polyacrylonitrile nanofibers with enhanced performance for lithium-ion storage. ACS Omega, 2021, 6, 2542-2548. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.0c04326.
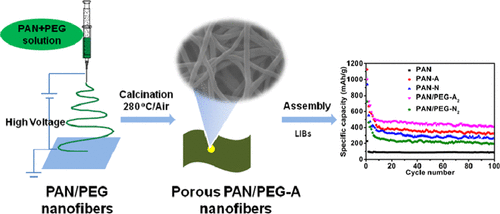
■ An integrated approach merging template-assisted electrospinning with heat treatment was utilized to produce porous polyacrylonitrile (PAN) nanofibers endowed with surface functionalities. Due to their rich oxygen functionalities and porous architecture, these nanofibers showcased superior capacity, impressive rate performance, and prolonged cycle life (418 mA h g-1 at 50 mA g-1 after 300 cycles), significantly outperforming the original PAN precursors.
7. Bajpai M*, Kadier A, Katoch SS, Ma PC. Treatment of pharmaceutical wastewater containing cefazolin by electrocoagulation (EC): Optimization of various parameters using response surface methodology (RSM), kinetics, and isotherms. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 2021, 176, 254-266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cherd.2021.10.012.
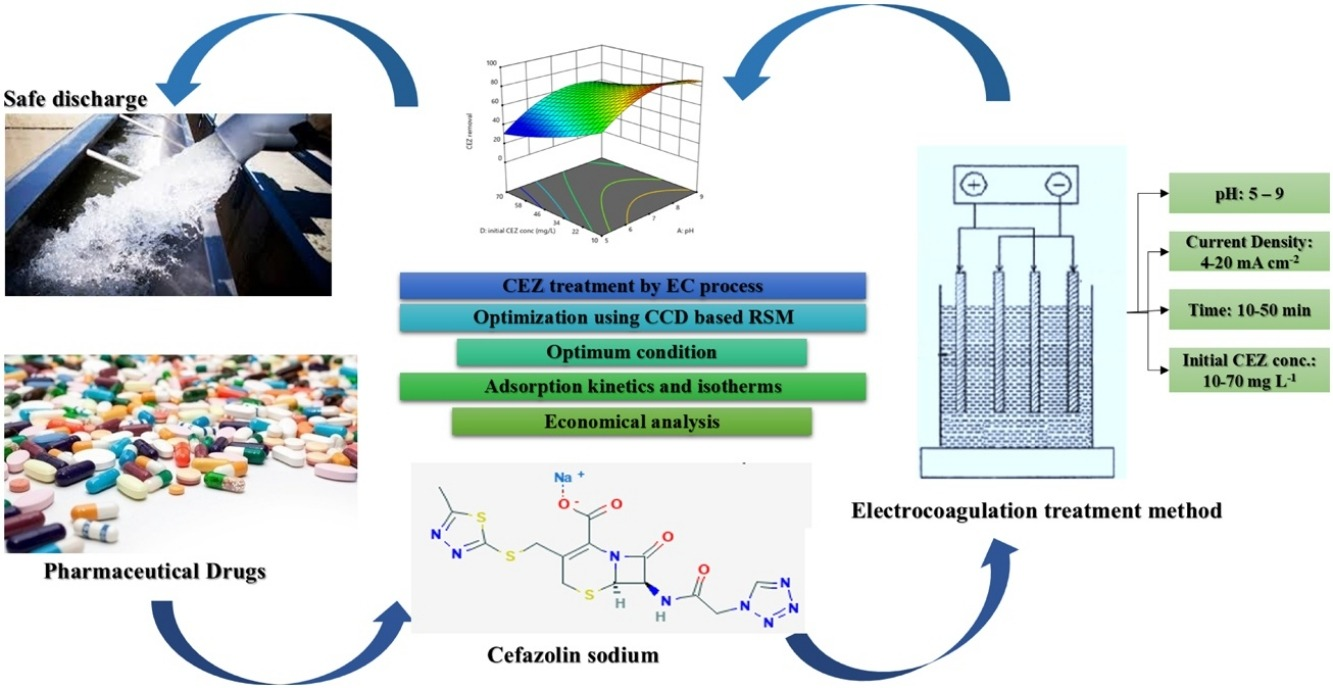
■ The removal of cefazolin (CEZ) using the electrocoagulation method was explored on a batch scale, focusing on the effects of pH, current density, electrocoagulation time, and initial CEZ concentration. Response surface methodology with a central composite design was employed for the investigation. The study also included an analysis of the equilibrium adsorption behavior through Langmuir and Freundlich isotherms, alongside an evaluation of coagulant adsorption kinetics via first and second-order kinetic models.
8. Kadier A, Ilyas RA*, Huzaifah MRM*, Harihastuti N, Sapuan SM, Harussani MM, Azlin MNM, Yuliasni R, Ibrahim R, Atikah MSN, Wang J, Chandrasekhar K, Islam MA, Sharma S, Punia S, Rajasekar A*, Asyraf MRM, Ishak MR. Use of industrial wastes as sustainable nutrient sources for bacterial cellulose (BC) production: Mechanism advances and future perspectives. Polymers, 2021, 13, 3365. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13193365.
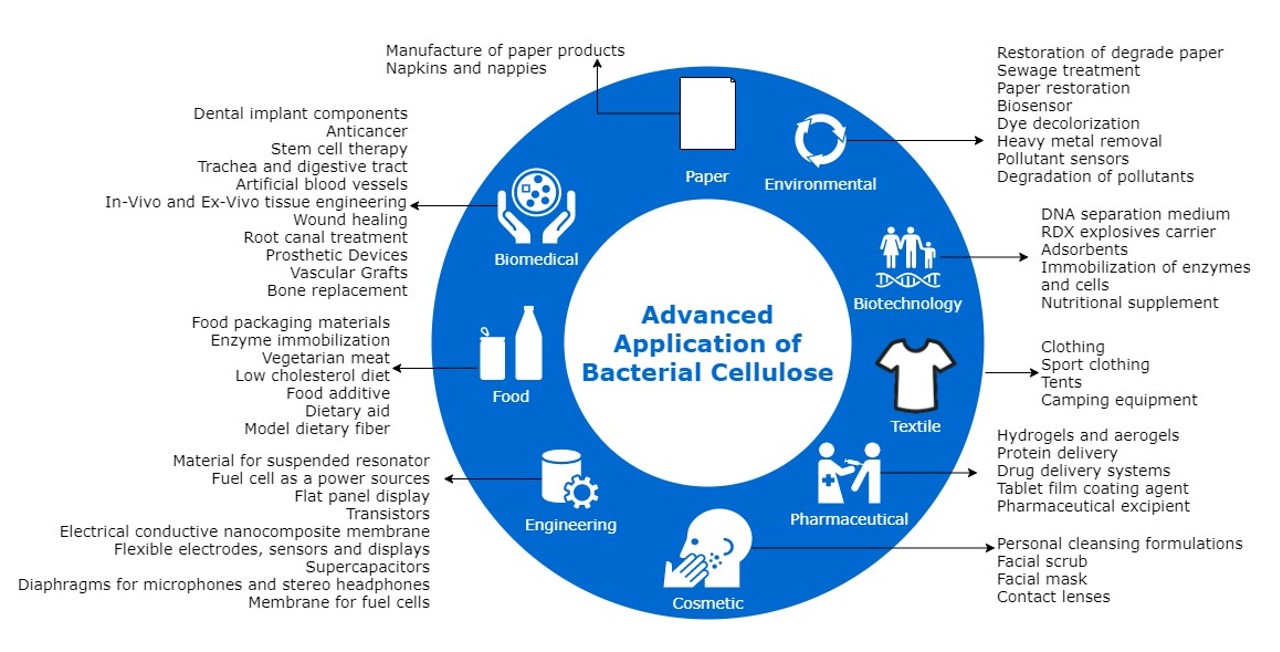
■ The technical and economic viability of producing microbial cellulose (BC) from various industrial wastes, including those from agroindustry, textile, biodiesel production, micro-algae biomass, wastewater sugar, lignocellulosic biorefineries, breweries, and beverage sectors, are reviewed. It concludes that these wastes hold significant potential for high BC concentrations by optimizing bacterial culture conditions like temperature and pH.
9. Moussavi SP, Kadier A, Zaidi NS, Aryanti PTP, Nugroho FA, Wang J, Ma PC*. Removal of phosphorus from aqueous solution using multi-wall carbon nanotube (MWCNT) as adsorbent: Kinetics and isotherms. Fullerenes, Nanotubes and Carbon Nanostructures, 2022, 30 (5), 589-595. https://doi.org/10.1080/1536383X.2021.1979968.
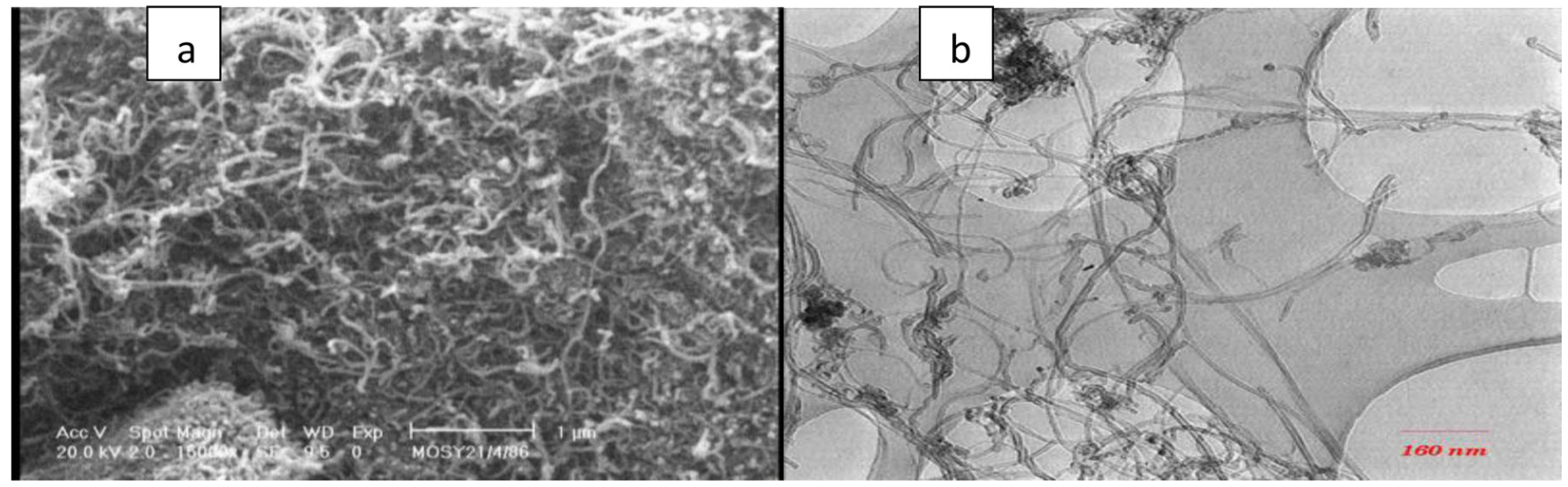
■ Multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) are an affordable and eco-friendly adsorbent for removing phosphorus from aqueous solutions using municipal wastewater samples that have been evaluated. Parameters such as pH, adsorbent and phosphorus concentrations, and contact time were optimized. For the first time, phosphorus adsorption kinetics and isotherms on MWCNTs were explored, enhancing understanding of the process.
10. Jayaraman N, Ananthaselvam A, Alsalhi MS*, Devanesan S, Kadier A*, Murali Kannan M, Rajasekar A*. Effect of crude methanolic extract of Lawsonia inermis for anti-biofilm on mild steel 1010 and its effect on corrosion in a re-circulating wastewater system. Journal of King Saud University-Science, 2021, 33, 101611. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksus.2021.101611.
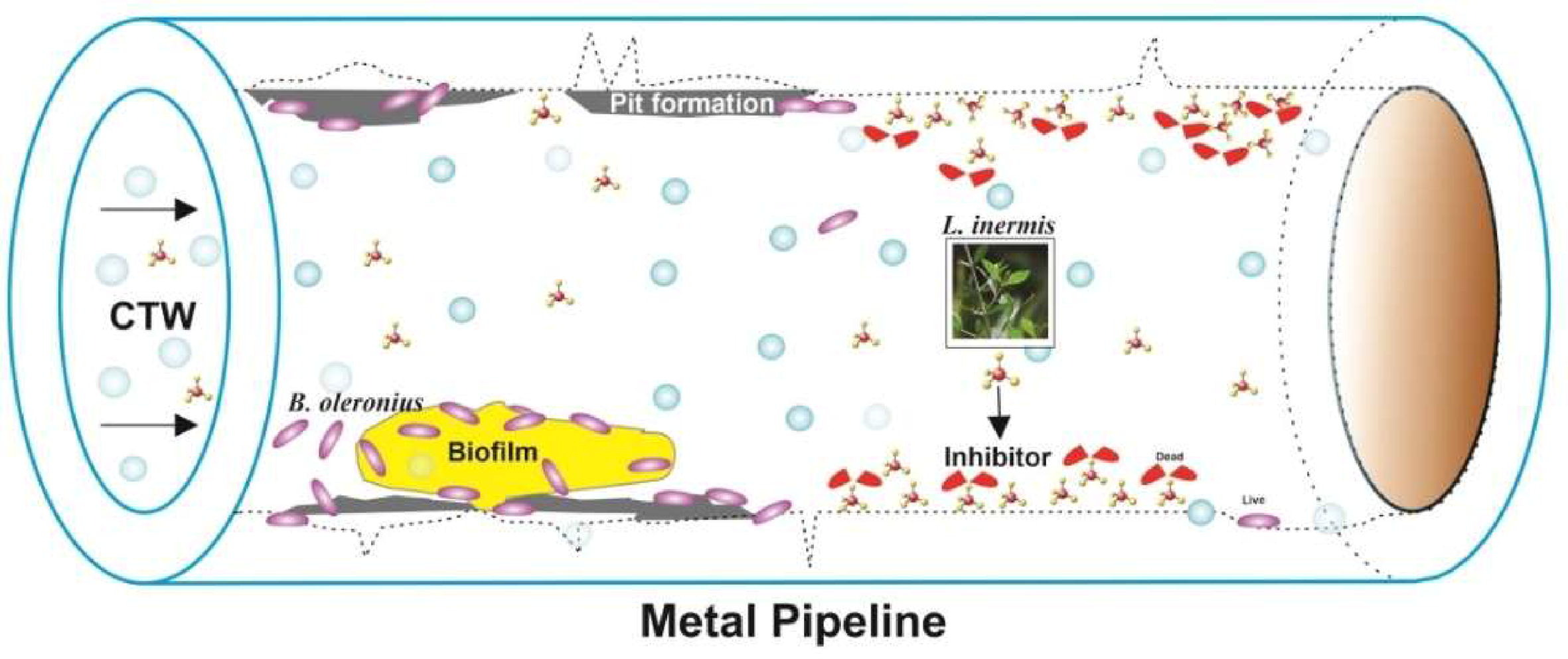
■ The effectiveness and mechanism of green corrosion inhibitors (GCI) for controlling microbiologically induced corrosion (MIC) in re-circulating water systems were validated through weight loss measurements, electrochemical studies, and surface morphology analysis. This research confirms the utility of GCIs in mitigating MIC.
11. Eslami, A*, Kashani, MR, Khodadadi, A, Varank, G, Kadier, A*, Ma, PC, Madihi-Bidgoli, S, Ghanbari, F* Sono-peroxi-coagulation (SPC) as an effective treatment for pulp and paper wastewater: Focus on pH effect, biodegradability, and toxicity. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 2021, 44, 102330. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2021.102330.
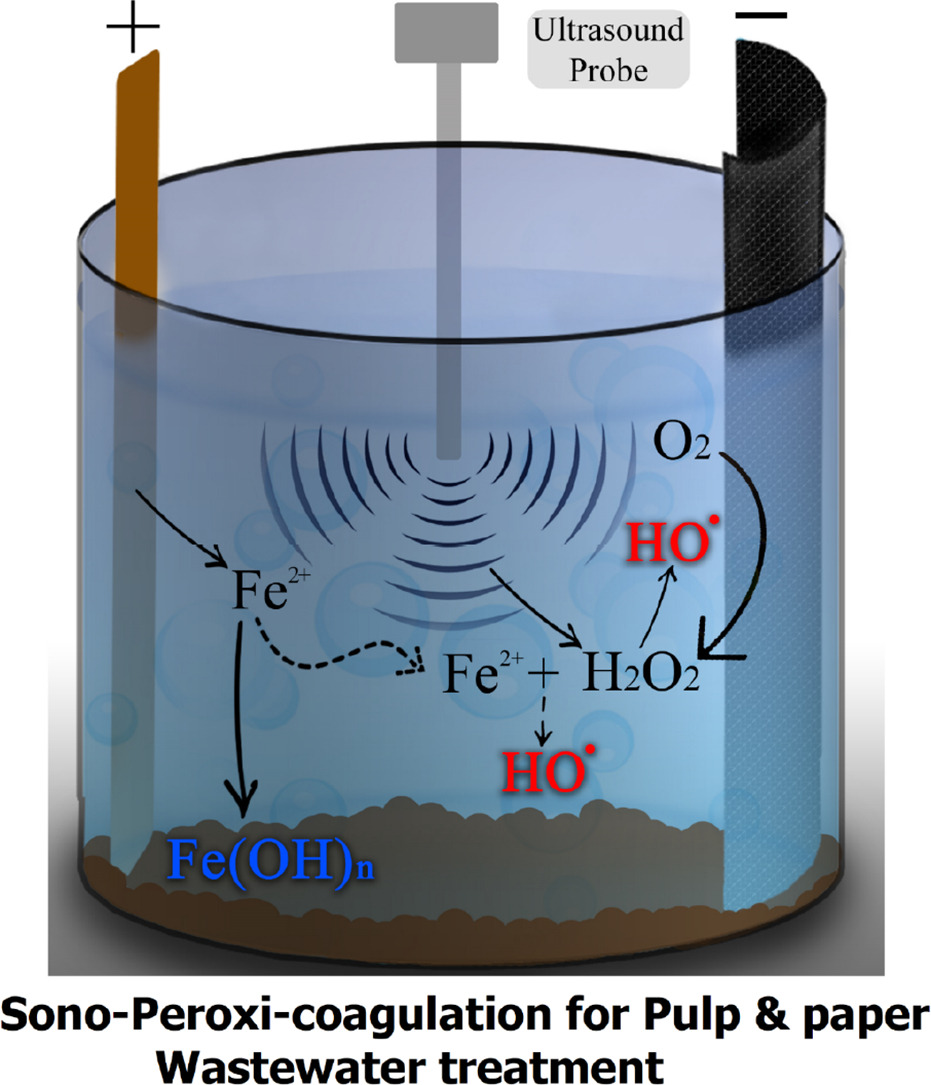
■ Operational parameters, including electrolysis time, applied current, and pH, were evaluated for their impact on COD reduction via the sono-peroxi-coagulation process. Organic oxidation was assessed using the BOD/COD ratio and average oxidation state. The study further examined the influence of process conditions and pH on PPWW’s biodegradability and COD removal efficiency, comparing the synergistic effects of SPC with US-assisted EF and PC processes under optimal conditions.
12. Gutnikov, SI*, Popov, SS, Efremov, VA, Ma, PC, Lazoryak, BI. Correlation of phase composition structure and mechanical properties of natural basalt continuous fibers. Natural Resources Research. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11053-020-09786-1.
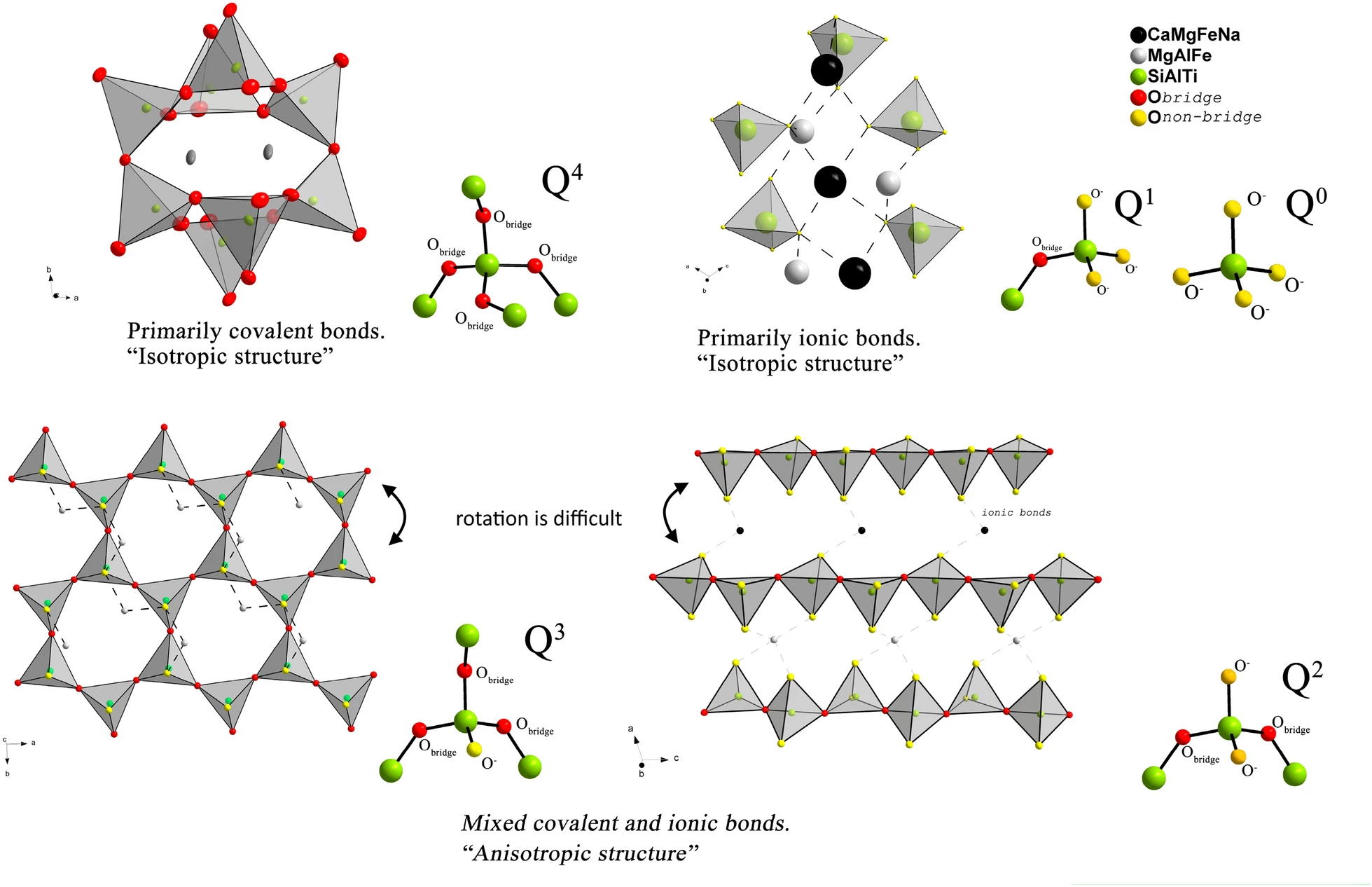
■ The impact of phase composition, acidity modulus, and NBO/T ratio of basalt rocks on the tensile strength and elastic modulus of basalt continuous fibers from 14 different deposits are reported. Phase composition was determined using the Rietveld method, identifying tectosilicates and inosilicates as main components.
附件下载: