2020
1. Lv P, Yasin A, Hao B, Ma PC*. Wheat bran/polymer composites as a solidifier to gel oil on water surface. Composites Communications, 2020, 22, 100471. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coco.2020.100471.

■ A polymer-based oil gelling agent (OGA) was developed utilizing wheat bran, a byproduct of flour milling. The OGA possessed a multi-scale porous structure, exhibiting excellent hydrophobic and oleophilic performance, and could absorb various oily compounds by 4.9-12.0 times its own weight.
2. Cai DL, Yue X*, Hao B, Ma PC*. A sustainable poly(vinyl chloride) plasticizer derivated from waste cooking oil. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2020, 274, 122781. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.122781.
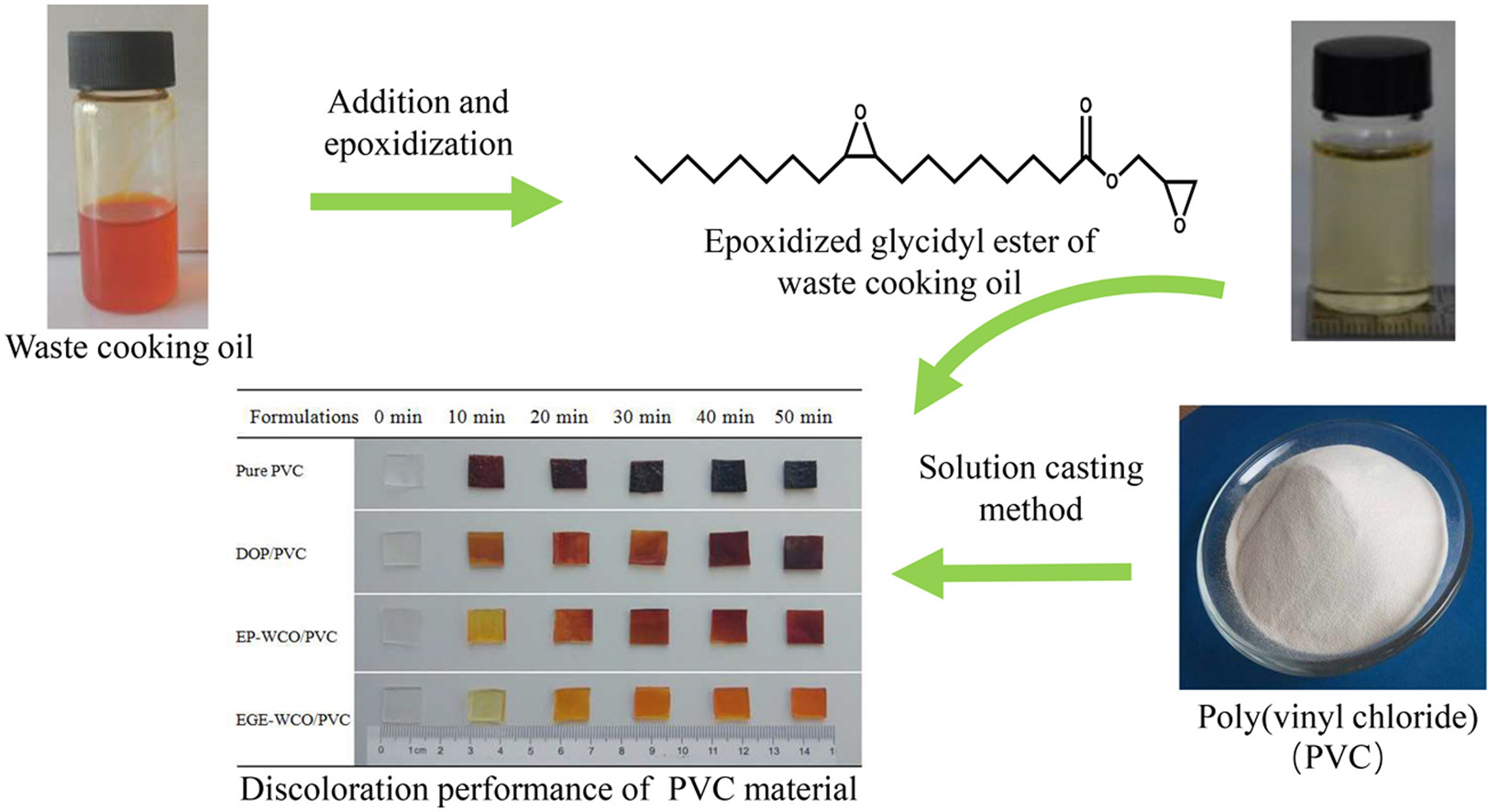
■ A renewable plasticizer originated from waste cooking oil (WCO) was reported. The plasticizing effect of the developed material on the properties of poly(vinyl chloride) (PVC) was studied. The results showed that epoxy groups were covalently bonded on the fatty acid derived from WCO through the addition and epoxidization reactions. Compared with commercial dioctyl phthalate plasticizers, the plasticizer developed in this study improved the thermal stability and flexibility of PVC along with a lower glass transition temperature.
3. Chang C, Yue X, Hao B, Xing D, Ma PC*. Direct growth of carbon nanotubes on basalt fiber for the application of electromagnetic interference shielding. Carbon, 2020, 167, 31-39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2020.05.074.
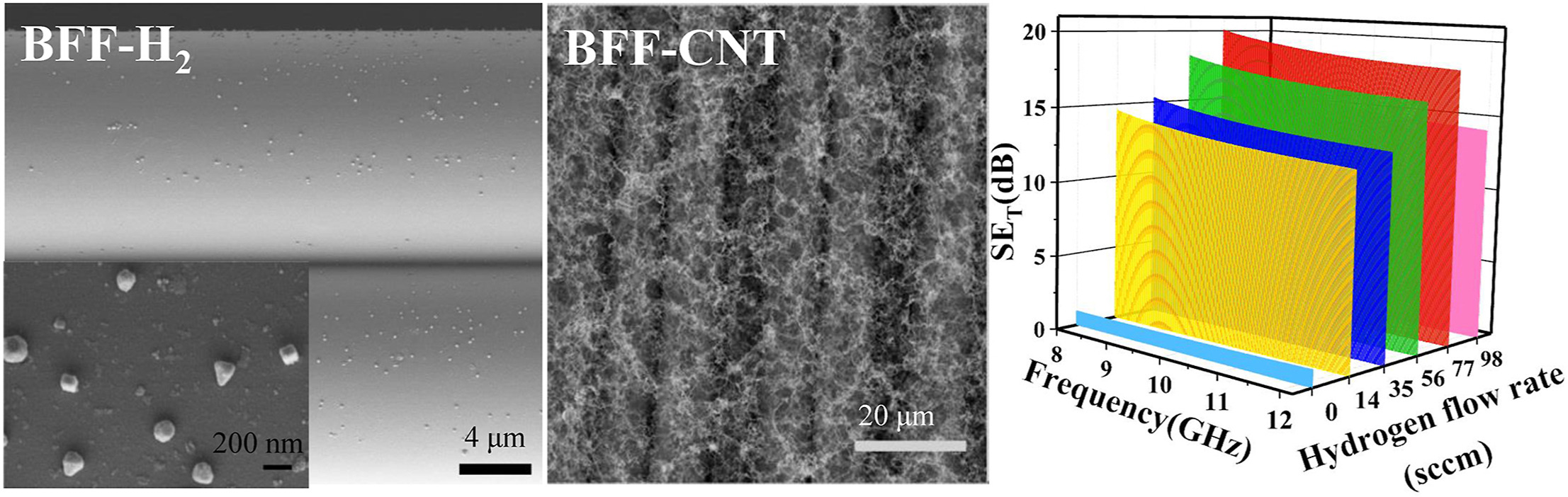
■ A composite material was reported combining basalt fiber fabric and carbon nanotubes (CNTs) to enhance electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding. Different techniques were employed to study the morphologies and properties of the fabric and corresponding nanocomposites.
4. Ma Q, Hao B, Ma PC*. Modulating the sensitivity of a flexible sensor using conductive glass fibre with a controlled structure profile. Composites Communications, 2020, 20, 100367. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coco.2020.100367.
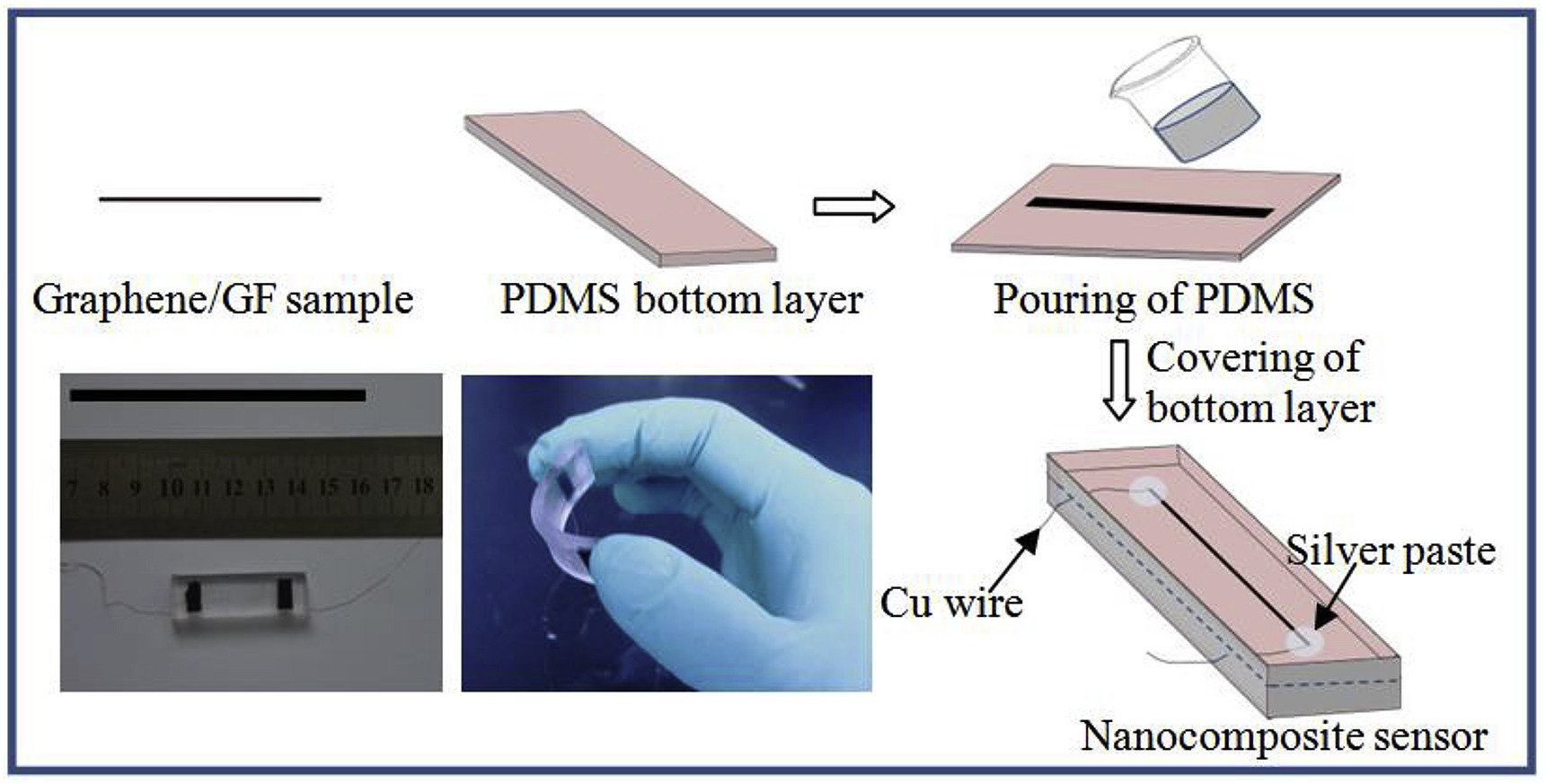
■ A flexible sensor with graphene-coated glass fiber in a PDMS matrix, fine-tuning its sensitivity by adjusting the fiber’s embedded depth, was reported. Sensitivity varied with bending direction and embedding depth, achieving a peak gauge factor of 7.3 at a 68° bend, equivalent to a 2.2% tensile strain.
5. Zhang YR, Chen JT, Hao B*, Wang R, Ma PC*. Preparation of cellulose-coated cotton fabric and its application for the separation of emulsified oil in water. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2020, 240, 116318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.116318.

■ A multi-functional fabric combining cellulose with commercial cotton was developed, demonstrating significant enhancements in strength, thermal stability, and hydrophilic performance due to a NaOH/urea dissolution and salt solution regeneration process. Such modification significantly enhanced the fabrics' strength, thermal stability, and hydrophilic performance.
6. Miao YC, Xing D, Xi XY, Yue X*, Bai YX, Ma PC*. Development of conducting basalt fibre with polymer-based nanocomposite sizing. Materials Today Communications, 2020, 23, 101170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2020.101170.

■ Epoxy-based polymer nanocomposites with carbon nanotubes were developed as a sizing agent for basalt fiber, enhancing its electrical and mechanical properties. An optimal sizing formulation was achieved through a comprehensive experiment involving two factors and four levels, focusing on stability, wettability, conductivity, and morphology.
7. Ma Q, Hao B, Ma PC*. Flexible sensor based on polymer nanocomposites reinforced by carbon nanotube foam derivated from cotton. Composites Science and Technology, 2020, 192, 108103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compscitech.2020.108103.

■ CNT foam and corresponding nanocomposites were prepared via a monomer infusion process to tackle nanofiller dispersion and re-agglomeration challenges in polymer matrices. Cotton templates facilitated the growth of CNTs on carbonized fibers, yielding foam-like structures with exceptional hydrophobicity and absorption qualities.
8. Meng B, Zhang Y, Ma PC*. Composites with AIEgens for temperature sensing and strain measurement. Macromolecular Chemistry and Physics, 2020, 1900552. https://doi.org/10.1002/macp.201900552.
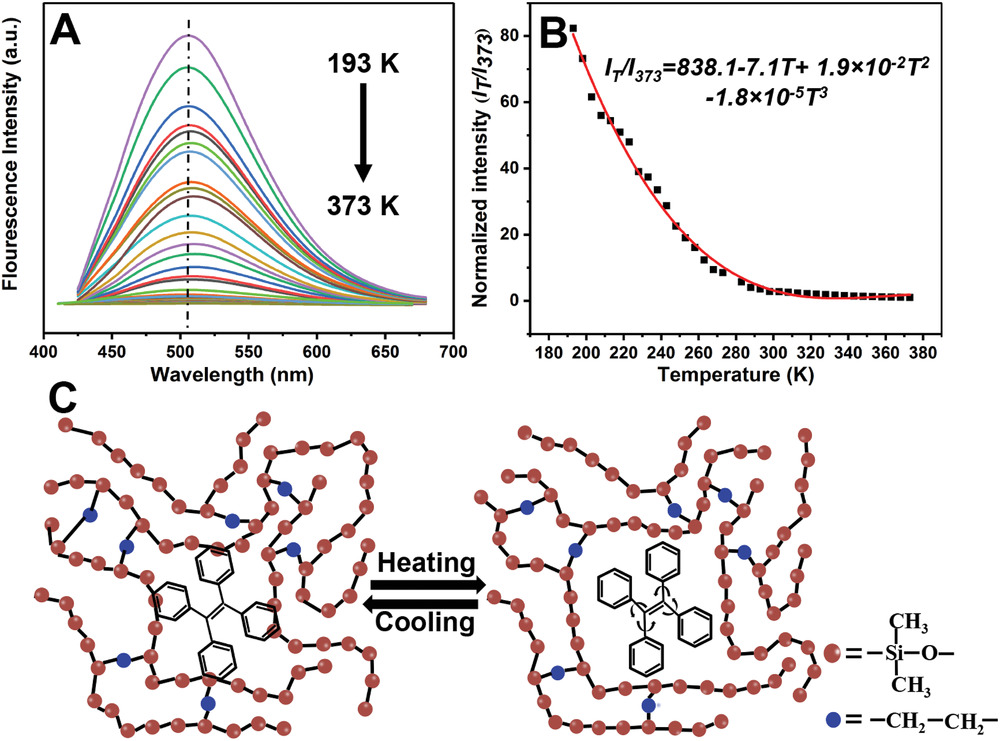
■ Polymer composites blending tetraphenylethene with aggregation-induced emission (AIE) properties and polydimethylsiloxane were developed. The composites exhibit unique, concentration-dependent fluorescent emissions attributed to AIEgen’s transition from crystal to amorphous state. This fluorescence is markedly sensitive to external stimuli such as temperature and mechanical stress, showcasing a decrease in intensity under higher temperatures or mechanical force.
9. Yang L, Liu J, Yang L, Zhang M, Zhu H, Wang F, Yin J*. Co3O4 imbedded g-C3N4heterojunction photocatalysts for visible-light-driven hydrogen evolution. Renewable Energy, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2019.06.072.
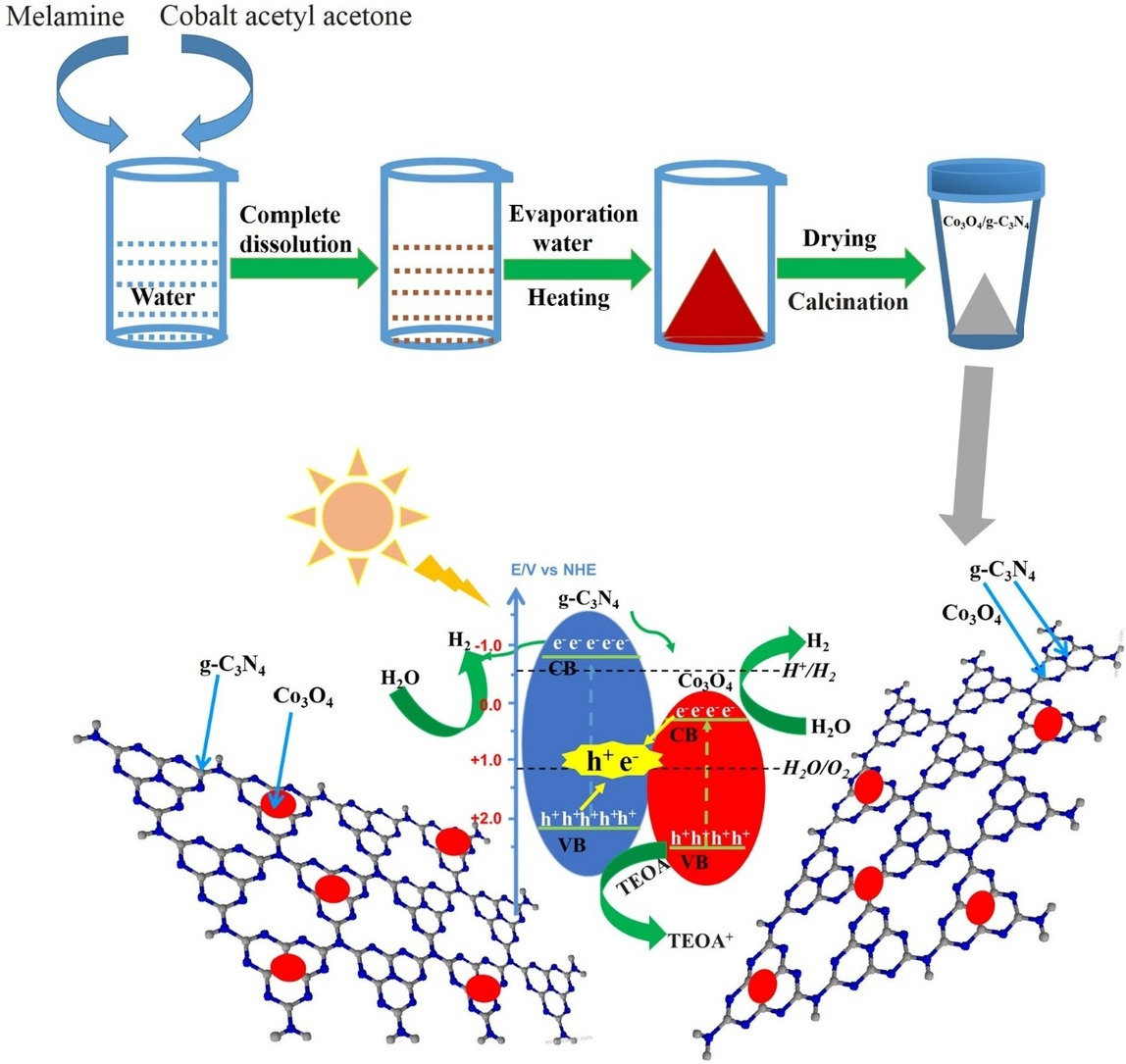
■ The Co3O4/g-C3N4 heterojunction photocatalysts were synthesized via a simple aqueous process, achieving homogeneous Co3O4 dispersion within the g-C3N4 matrix up to 3 wt.%. The optimal 1 wt.% Co3O4 loading enhanced the hydrogen evolution rate to 50 μmol h-1 g-1, fivefold that of pure components. This strategy highlights a green approach to enhancing photocatalytic activities.
10. Xue N, Liu J, Wang P, Wang C, Li S, Zhu H*, Yin J*. Scalable synthesis of Fe3N nanoparticles within N-doped carbon frameworks as efficient electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction reaction. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2020, 580, 460-469. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2020.07.005.
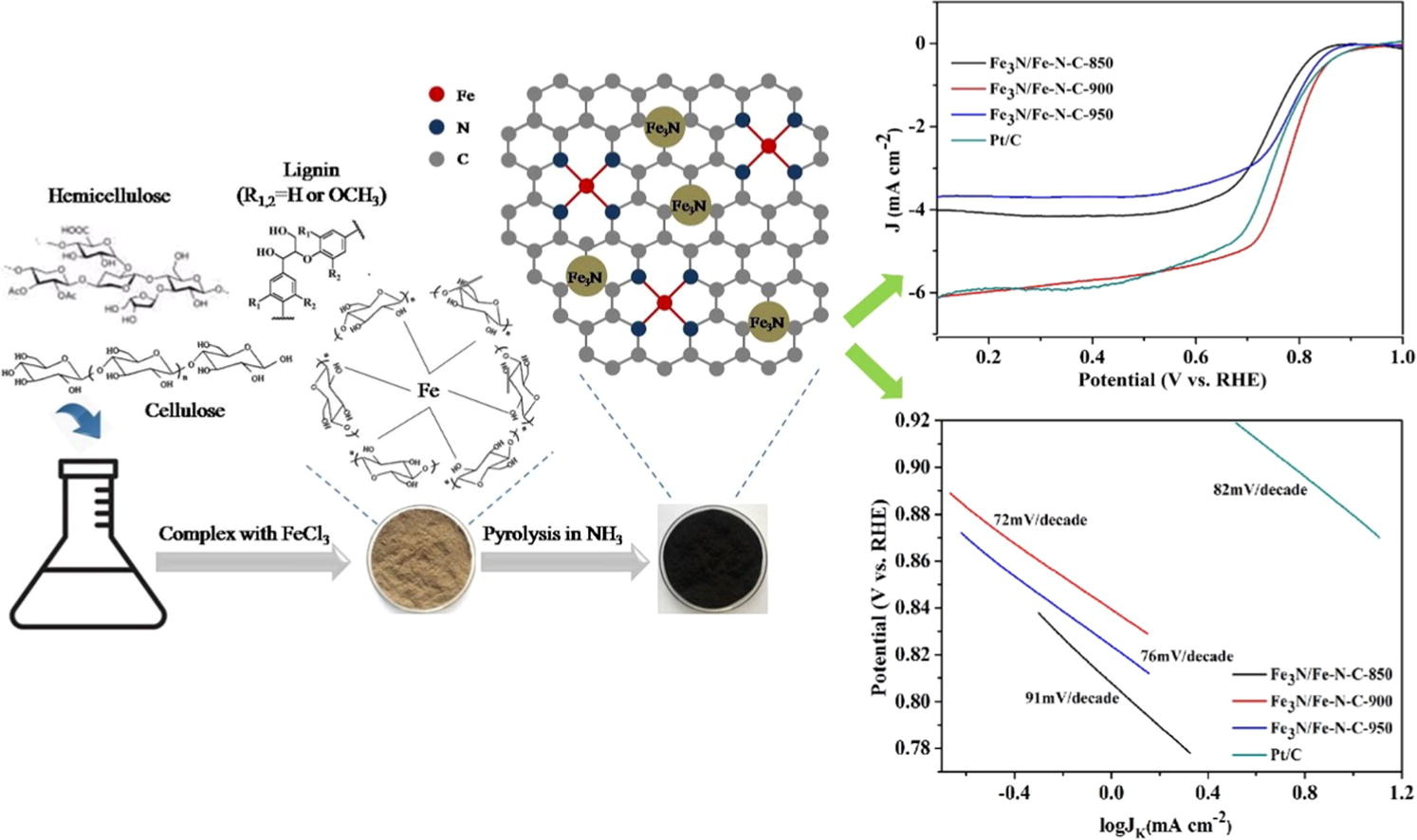
■ A highly active ORR electrocatalyst, Fe3N/Fe-N-C, was developed from walnut shell precursors, featuring both Fe3N nanoparticles and Fe-N-C active sites within N-doped carbon frameworks. This synthesis involved iron ion incorporation and subsequent pyrolysis in an NH3 atmosphere. XRD, TEM, and XPS analyses confirmed the coexistence of Fe3N and Fe-N-C. This research introduces a cost-effective, scalable alternative to Pt-based catalysts, offering a versatile approach for large-scale production suitable for practical applications.
11. Yang L, Wang P, Zhang S, Wang Y, Zang L, Zhu H, Yin J*, Yang HY*. Flexible and additive-free organic electrodes for aqueous sodium ion batteries. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2020, 8, 22791-22801. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0TA07267B.
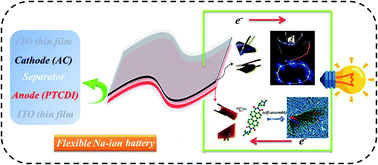
■ An interfacial self-assembly strategy was introduced to fabricate PTCDI nanofibers directly onto flexible ITO substrates without binders. This method, supported by in-situ Raman spectroscopy and DFT calculations, clarifies the Na+ storage mechanism via the enolization reaction of carbonyl groups in PTCDI. The organic nanofibers exhibit remarkable volumetric energy and power densities, making them highly suitable for various applications in flexible electronics that utilize organic electrode materials in aqueous neutral electrolytes.
12. 邢丹, 葸雄宇, 郭泽世, 岳秀, 郝斌, 梁存光, 顾轶卓, 陈涛,王瑞, 马鹏程*. 模拟月壤制备连续纤维的可行性研究. 中国科学: 技术科学, 2020, 50, 1625-1633.
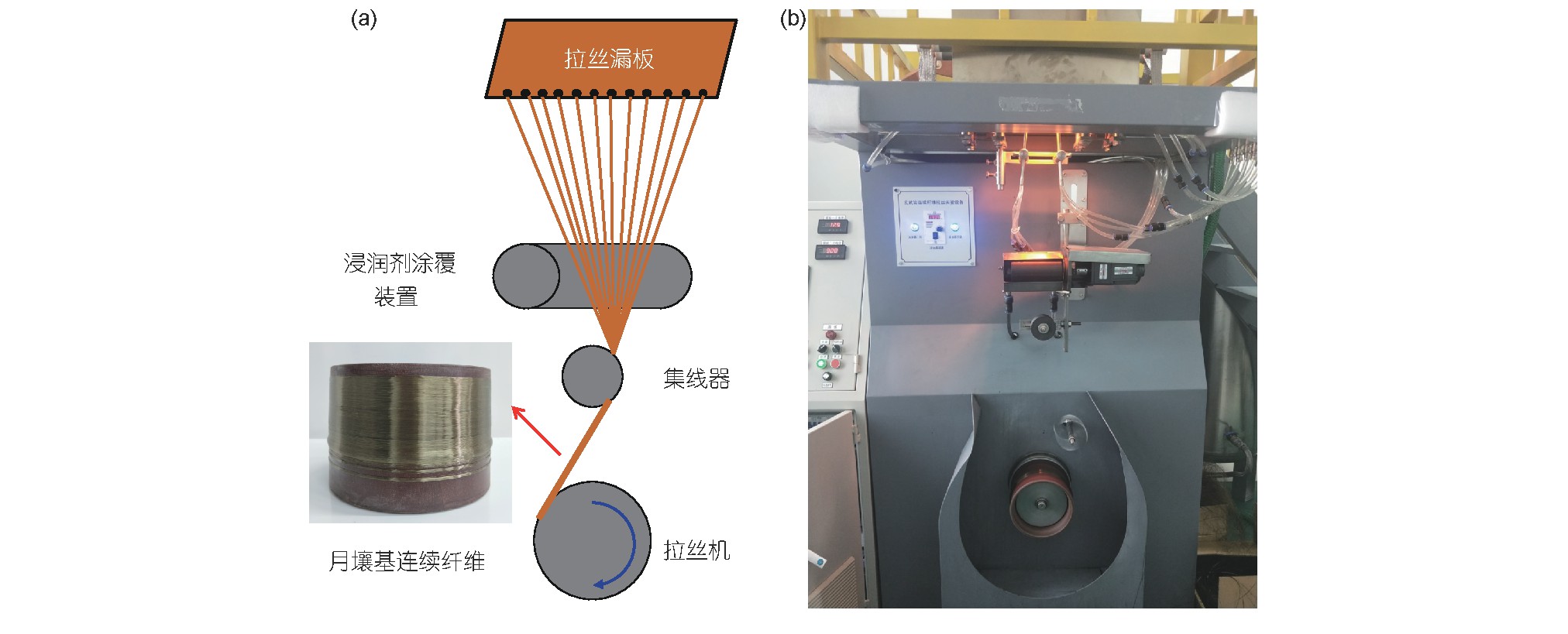
■ 月球基地建设是人类开展深空探测的初步任务,原位利用月球资源对于实现月球基地建设具有重要意义。以月球基地建设中对高性能材料的需求为出发点,研究了模拟月壤的组成、晶相结构、熔融特征和成纤行为。研究结果表明,月壤与地球玄武岩矿石具有相近的化学成分和矿物相组成,模拟月壤在1332℃完全熔融并在淬冷后转化为非晶态玻璃体.采用熔融-牵引法获得了单丝拉伸强度超过1400 MPa的月壤基连续纤维,该强度接近目前商业化的玄武岩纤维。研究结果证实原位利用月壤制备连续纤维具有一定的可行性,基于月壤纤维增强的复合材料有望为未来月球基地建设提供原材料保障。
附件下载: